Page 77 - PC 101 practical notes 24-25..
P. 77
MANSOURA NATIONAL UNIVERSIY
PHARM D- CLINICAL PHARMACY LEVEL I PHARM. ANAL. CHEM. I (PC 101)
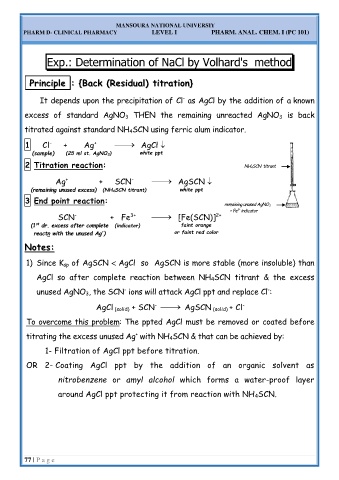
Exp.: Determination of NaCl by Volhard's method
P Pr ri in nc ci ip pl le e : : { {B Ba ac ck k ( (R Re es si id du ua al l) ) t ti it tr ra at ti io on n} }
It depends upon the precipitation of Cl as AgCl by the addition of a known
-
excess of standard AgNO 3 THEN the remaining unreacted AgNO 3 is back
titrated against standard NH 4SCN using ferric alum indicator.
1 Cl + Ag ⎯→⎯ AgCl
+
-
(sample) (25 ml st. AgNO 3) white ppt
2 Titration reaction: NH 4SCN titrant
⎯
Ag + SCN ⎯→ AgSCN
-
+
(remaining unused excess) (NH 4SCN titrant) white ppt
3 End point reaction: remaining unused AgNO 3
3+
+ Fe indicator
SCN + Fe ⎯→ [Fe(SCN)]
⎯
2+
-
3+
st faint orange
(1 dr. excess after complete (indicator)
+
reactn with the unused Ag ) or faint red color
N No ot te es s: :
1) Since K sp of AgSCN AgCl so AgSCN is more stable (more insoluble) than
AgCl so after complete reaction between NH 4SCN titrant & the excess
-
unused AgNO 3, the SCN ions will attack AgCl ppt and replace Cl :
-
-
⎯
-
AgCl (solid) + SCN ⎯→ AgSCN (solid) + Cl
To overcome this problem: The ppted AgCl must be removed or coated before
titrating the excess unused Ag with NH 4SCN & that can be achieved by:
+
1- Filtration of AgCl ppt before titration.
OR 2- Coating AgCl ppt by the addition of an organic solvent as
nitrobenzene or amyl alcohol which forms a water-proof layer
around AgCl ppt protecting it from reaction with NH 4SCN.
77 | P a g e