Page 127 - ebook HCC
P. 127
PROGRAMME AND ABSTRACTSAND ABSTRACTS
GENEVA, SWITZERLANDA, SWITZERLAND
EASL HCC SUMMITHCC SUMMIT
125
124 PROGRAMME GENEV EASL 125
124
FEBRUARY 13 - 16, 2014Y 13 - 16, 2014
FEBRUAR
Poster Board Number B21
QUANTITATIVE PHOSPHOPROTEOME ANALYSIS Conclusions: We have identified phosphopeptides signatures in human samples of
OF HUMAN HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMAS nfHCC that led to the identification of a deregulated PDK-dependent network in those
tumors. The elucidation of the functional causes and consequences of such deregulation
DEVELOPED ON NON-FIBROTIC LIVER is ongoing.
Luc Negroni , Daniela Arma , Saïd Taouji , Violaine Moreau , Charles Balabaud ,
2
2
2
2
1
Paulette Bioulac-Sage , Jean-Marie Schmitter , Jean Rosenbaum , Eric Chevet 2
1
2
2
1 UMR 5248, Centre de Génomique Fonctionnelle, Université de Bordeaux, INSERM
2
U1053, Université Bordeaux Segalen, Bordeaux, France
Corresponding author’s e-mail: jean.rosenbaum@inserm.fr
Introduction: Ten to 40% hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) arise on non-cirrhotic liver,
including 5% on non-fibrotic liver (nfHCC). These tumors provide an interesting model
for the analysis of the hepatocarcinogenesis pathways without the confounding factors
associated with cirrhosis. Carcinogenesis has been often associated with the deregulation
of signaling pathways that involve a number of phosphorylation cascades. Quantitative
phosphoproteomics allows the global analysis of these events, but has never been used
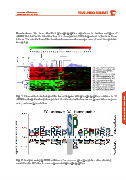
in a large number of human HCC. Fig. 1. Hierarchical clustering of the livers biopsies with phosphopeptides common to 18
BASIC POSTER ABSTRACTS Aims: Our aim was to use quantitative phosphoproteomics on a series of nfHCC samples, color, under-representation. BASIC POSTER ABSTRACTS
nfHCC and significatively deregulated. A red color indicates over-representation, a green
thereby allowing the discovery of deregulated kinase cascades, and to validate some
of those on larger cohorts using medium throughput analytical tools (Alphascreen® and
AMMP®).
Methodology: Tumors were defined as nfHCC when the non-tumor livers were classified
as F0 or F1 according to METAVIR. We used 18 surgical samples from nfHCC, and 6
samples of histologically normal liver as controls. Proteins were extracted and digested
with trypsin, phosphopeptides were purified on Ti02 matrices and labeled with iTRAQ
8-plex reagents for quantitative analysis on LTQ-Orbitrap XL. In addition 80 tumor and 20
non–tumor samples were analyzed for the activation status of select signaling pathways
such as ERK using Alphascreen® and AMMP®.
Results: A total of 315 different phosphopeptides were quantified in the whole series
of samples, and the analysis was focused on the 65 that were common in the 3 series
of 6 tumors. Non-supervised hierarchical clustering separated the HCC from the non-
HCC groups (Fig. 1). Nineteen phosphopeptides were significantly more represented in
nfHCC than in controls, and 15 less abundant. Motif analysis showed that a consensus
site for proline-directed kinases (PDK) was significantly enriched (p < 0.05, Fig. 2) in over- Fig. 2. Analysis using pLOGO software of consensus phosphorylation sites showing
represented phosphopeptides. Because MAPK are prototypic PDKs and are deregulated enrichment in SP sites in over-represented phosphopeptides.
in many cancers, we analyzed their activation in a series of 80 nfHCC as compared to 20
non-tumor samples and found an overall increased activity in nfHCC samples.