Page 14 - Confined Space Training - Student Manual 2021
P. 14
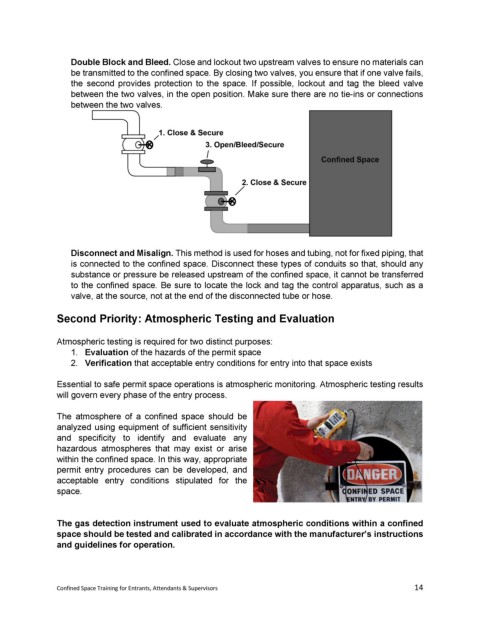
Double Block and Bleed. Close and lockout two upstream valves to ensure no materials can
be transmitted to the confined space. By closing two valves, you ensure that if one valve fails,
the second provides protection to the space. If possible, lockout and tag the bleed valve
between the two valves, in the open position. Make sure there are no tie-ins or connections
between the two valves.
Disconnect and Misalign. This method is used for hoses and tubing, not for fixed piping, that
is connected to the confined space. Disconnect these types of conduits so that, should any
substance or pressure be released upstream of the confined space, it cannot be transferred
to the confined space. Be sure to locate the lock and tag the control apparatus, such as a
valve, at the source, not at the end of the disconnected tube or hose.
Second Priority: Atmospheric Testing and Evaluation
Atmospheric testing is required for two distinct purposes:
1. Evaluation of the hazards of the permit space
2. Verification that acceptable entry conditions for entry into that space exists
Essential to safe permit space operations is atmospheric monitoring. Atmospheric testing results
will govern every phase of the entry process.
The atmosphere of a confined space should be
analyzed using equipment of sufficient sensitivity
and specificity to identify and evaluate any
hazardous atmospheres that may exist or arise
within the confined space. In this way, appropriate
permit entry procedures can be developed, and
acceptable entry conditions stipulated for the
space.
The gas detection instrument used to evaluate atmospheric conditions within a confined
space should be tested and calibrated in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions
and guidelines for operation.
Confined Space Training for Entrants, Attendants & Supervisors 14