Page 216 - PhD GT
P. 216
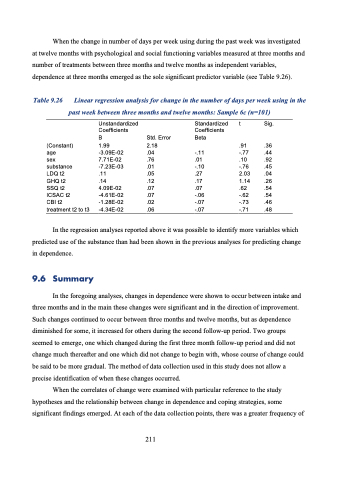
When the change in number of days per week using during the past week was investigated at twelve months with psychological and social functioning variables measured at three months and number of treatments between three months and twelve months as independent variables, dependence at three months emerged as the sole significant predictor variable (see Table 9.26).
Table 9.26 Linear regression analysis for change in the number of days per week using in the past week between three months and twelve months: Sample 6c (n=101)
Unstandardized Coefficients
B
1.99
-3.09E-02 7.71E-02 -7.23E-03 .11
.14 4.09E-02 -4.61E-02 -1.28E-02 -4.34E-02
Standardized t Sig.
Coefficients Std. Error Beta
(Constant)
age
sex
substance
LDQ t2
GHQ t2
SSQ t2
ICSAC t2
CBI t2
treatment t2 to t3
2.18 .04 .76 .01 .05 .12 .07 .07 .02 .06
.91 .36 -.11 -.77 .44 .01 .10 .92 -.10 -.76 .45 .27 2.03 .04 .17 1.14 .26 .07 .62 .54 -.06 -.62 .54 -.07 -.73 .46 -.07 -.71 .48
In the regression analyses reported above it was possible to identify more variables which predicted use of the substance than had been shown in the previous analyses for predicting change in dependence.
9.6 Summary
In the foregoing analyses, changes in dependence were shown to occur between intake and three months and in the main these changes were significant and in the direction of improvement. Such changes continued to occur between three months and twelve months, but as dependence diminished for some, it increased for others during the second follow-up period. Two groups seemed to emerge, one which changed during the first three month follow-up period and did not change much thereafter and one which did not change to begin with, whose course of change could be said to be more gradual. The method of data collection used in this study does not allow a precise identification of when these changes occurred.
When the correlates of change were examined with particular reference to the study hypotheses and the relationship between change in dependence and coping strategies, some significant findings emerged. At each of the data collection points, there was a greater frequency of
211