Page 168 - Mathematics Coursebook
P. 168
17.3 Translating shapes
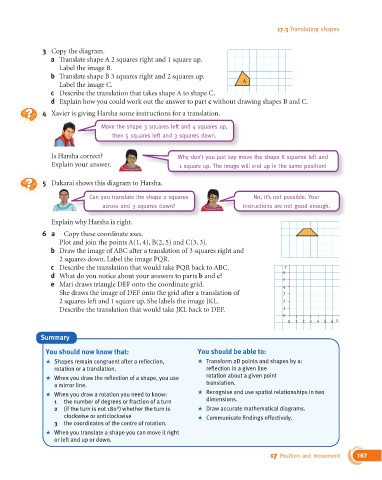
3 Copy the diagram.
a Translate shape A 2 squares right and 1 square up.
Label the image B.
b Translate shape B 3 squares right and 2 squares up.
Label the image C. A
c Describe the translation that takes shape A to shape C.
d Explain how you could work out the answer to part c without drawing shapes B and C.
4 Xavier is giving Harsha some instructions for a translation.
Move the shape 3 squares left and 4 squares up,
then 5 squares left and 3 squares down.
Is Harsha correct? Why don’t you just say move the shape 8 squares left and
Explain your answer. 1 square up. The image will end up in the same position!
5 Dakarai shows this diagram to Harsha.
Can you translate the shape 2 squares No, it’s not possible. Your
across and 3 squares down? instructions are not good enough.
Explain why Harsha is right.
6 a Copy these coordinate axes.
Plot and join the points A(1, 4), B(2, 5) and C(3, 3).
b Draw the image of ABC after a translation of 3 squares right and
2 squares down. Label the image PQR.
c Describe the translation that would take PQR back to ABC. y
d What do you notice about your answers to parts b and c? 6 5
e Mari draws triangle DEF onto the coordinate grid. 4
She draws the image of DEF onto the grid after a translation of 3
2 squares left and 1 square up. She labels the image JKL. 2
Describe the translation that would take JKL back to DEF. 1
0
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 x
Summary
You should now know that: You should be able to:
+ Shapes remain congruent after a reflection, + Transform 2D points and shapes by a:
rotation or a translation. reflection in a given line
+ When you draw the reflection of a shape, you use rotation about a given point
a mirror line. translation.
+ When you draw a rotation you need to know: + Recognise and use spatial relationships in two
1 the number of degrees or fraction of a turn dimensions.
2 (if the turn is not 180°) whether the turn is + Draw accurate mathematical diagrams.
clockwise or anticlockwise + Communicate findings effectively.
3 the coordinates of the centre of rotation.
+ When you translate a shape you can move it right
or left and up or down.
17 Position and movement 167