Page 10 - E-LKM ACID BASE_Neat
P. 10
Lembar Kerja Mahasiswa - Asam Basa
3. Lewis Theory
According to the Lewis definition, a molecule behaves as a base
when it donates a lone pair of electrons. Conversely, a molecule
behaves as an acid when it accepts a lone pair. So while the
Brønsted–Lowry definition focuses on the action of a proton, the Lewis
definition focuses on the action of a lone pair.
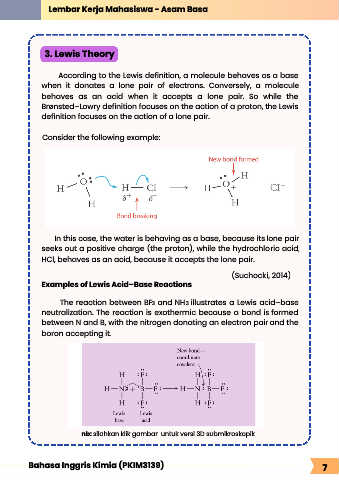
Consider the following example:
In this case, the water is behaving as a base, because its lone pair
seeks out a positive charge (the proton), while the hydrochloric acid,
HCl, behaves as an acid, because it accepts the lone pair.
(Suchocki, 2014)
Examples of Lewis Acid–Base Reactions
The reaction between BF and NH illustrates a Lewis acid–base
3
3
neutralization. The reaction is exothermic because a bond is formed
between N and B, with the nitrogen donating an electron pair and the
boron accepting it.
nb: silahkan klik gambar untuk versi 3D submikroskopik
Bahasa Inggris Kimia (PKIM3139) 7