Page 23 - NEA NEWHERE FLIPBOOK
P. 23
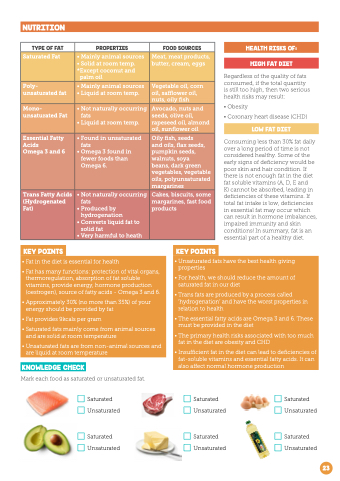
NUTRITION
TYPE OF FAT Saturated Fat
Poly- unsaturated fat Mono- unsaturated Fat
Essential Fatty Acids
Omega 3 and 6
Trans Fatty Acids
(Hydrogenated Fat)
KEY POINTS
PROPERTIES
• Mainly animal sources • Solid at room temp *Except coconut and palm oil
• Mainly animal sources • Liquid at room temp • Not naturally occurring fats • Liquid at room temp • Found in unsaturated fats • Omega 3 found in fewer foods than Omega 6
• Not naturally occurring fats • Produced by hydrogenation
• Converts liquid fat to solid fat • Very harmful to heath
FOOD SOURCES
Meat meat products butter cream eggs
Vegetable oil
corn oil
oil
safflower oil
oil
nuts oily fish
Avocado nuts and seeds olive oil
rapeseed oil
almond oil
oil
sunflower oil
oil
Oily fish
seeds and oils flax seeds pumpkin seeds walnuts soya
beans dark green vegetables vegetable vegetable oils polyunsaturated margarines
Cakes biscuits some margarines
fast food products KEY POINTS
HEALTH RISKS OF: HIGH FAT DIET
Regardless of of the quality of of fats consumed if the total quantity is still too high then two serious health risks may result:
• Obesity
• Coronary heart disease (CHD)
LOW FAT DIET
Consuming less than 30% fat daily over a long period of time is not considered healthy Some of the early signs of deficiency would be poor skin and hair condition If there is not enough fat in the the diet fat soluble vitamins (A D E and K) cannot be be absorbed leading in in deficiencies of these vitamins If total fat intake is low deficiencies in essential fat may occur which can result in hormone imbalances impaired immunity and skin conditions! In summary fat is an essential part of a a a a healthy diet • Fat
in the diet is essential for health • Fat
has many functions: protection of vital organs
thermoregulation absorption of fat soluble vitamins provide energy hormone production (oestrogen) source of fatty acids - Omega 3 and 6
• Approximately 30% (no more than 35%) of your energy should be provided by fat • Fat
provides 9kcals per gram
• Saturated fats mainly come
from animal sources and are solid at at room temperature • Unsaturated fats are from non-animal sources and are liquid at at room temperature KNOWLEDGE CHECK
Mark each food as saturated saturated or unsaturated fat Saturated Unsaturated Saturated Unsaturated • • • • • • Unsaturated fats have the best health giving properties
For health we should reduce the amount of saturated fat in our diet Trans fats are produced by a a a a a process called ‘hydrogenation’ and have the worst properties
in relation to health The The essential fatty acids are Omega 3 and 6
These must be provided in the diet The primary health risks associated with too much fat in the diet are obesity and CHD Insufficient fat in the diet can lead to deficiencies of fat-soluble vitamins and essential fatty acids It can also affect normal hormone production Saturated Unsaturated Saturated Unsaturated Saturated Unsaturated Saturated Unsaturated 23