Page 24 - NEA NEWHERE FLIPBOOK
P. 24
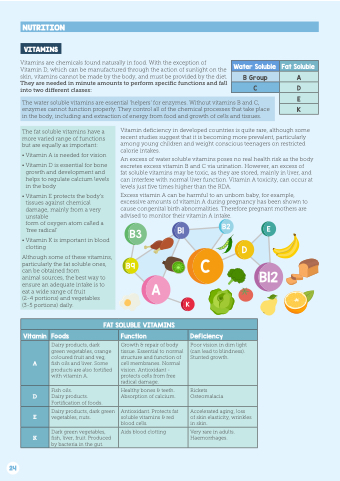
NUTRITION
VITAMINS
Vitamins are chemicals found naturally in in food With the exception of Vitamin D which can be manufactured through the the action of sunlight on on the the skin vitamins cannot be be made by by the the body and must be be provided by by the the diet They are needed in in minute amounts to perform specific functions and fall into two different classes:
Vitamin deficiency in in developed countries is quite rare although some recent studies suggest that it is becoming more prevalent particularly among young children and weight conscious teenagers on on on restricted calorie intakes An excess of water soluble vitamins poses no real health risk as the body excretes excess excess vitamin B and C via urination However an an excess excess of fat soluble vitamins may be toxic as they are stored mainly in in in liver and can can interfere with normal liver function Vitamin A toxicity can can occur at levels just five times higher than the RDA Excess vitamin A can be harmful to an an unborn baby for example excessive amounts of vitamin A during pregnancy has been shown to cause congenital birth abnormalities Therefore pregnant mothers are advised to to monitor their vitamin A intake Water Soluble
Fat Soluble
B Group
A C D E The water soluble vitamins vitamins are essential ‘helpers’ for enzymes Without vitamins vitamins B and C enzymes cannot function properly They control all of the chemical processes that take place in in in the body including and and and extraction of of energy from food and and and growth of of cells and and and tissues K
The fat soluble vitamins have a a a a more varied range of functions but are equally as important:
• Vitamin A is is needed for vision
• Vitamin D is essential for bone growth and and development and and helps to regulate calcium levels in the body • Vitamin E protects the body’s tissues against chemical damage mainly from a a a a very unstable
form of oxygen atom called a a a ‘free radical’
• Vitamin K
is important in in blood clotting
Although some of these vitamins particularly the fat soluble ones can be obtained from animal sources the best way to ensure an adequate intake is to eat a a a wide range of fruit (2-4 portions) and vegetables (3-5 portions) daily FAT SOLUBLE VITAMINS
Vitamin Foods
Function
Deficiency
A Dairy products dark green vegetables orange coloured fruit and veg fish oils and liver Some products are also fortified with vitamin A Growth & repair of body tissue Essential to normal structure and function of cell membranes Normal vision
Antioxidant - protects cells from free radical damage Poor vision
in dim light (can lead to blindness) Stunted growth D Fish oils Dairy products Fortification of foods
Healthy bones & teeth Absorption of calcium Rickets Osteomalacia
E Dairy products dark green vegetables nuts Antioxidant Protects fat soluble vitamins & red blood cells Accelerated aging loss of skin elasticity wrinkles in in skin K
Dark green vegetables fish liver fruit Produced by bacteria in the gut Aids blood clotting
Very rare in adults Haemorrhages 24