Page 17 - Kingdom Protist
P. 17
Members of the phylum Euglenophyta are
unicellular, plantlike protists called euglenoids.
Most euglenoids are found in shallow freshwater,
although some live in saltwater. Eugleanoids are
challenging to classify because they have
characteristics of both plants and animals. Most
euglenoids contain chloroplasts and
photosynthesize, which is characteristic of plants,
yet they lack a cell wall. Euglenoids also can be
heterotrophs. When light is not available for
photosynthesis, some can absorb dissolved
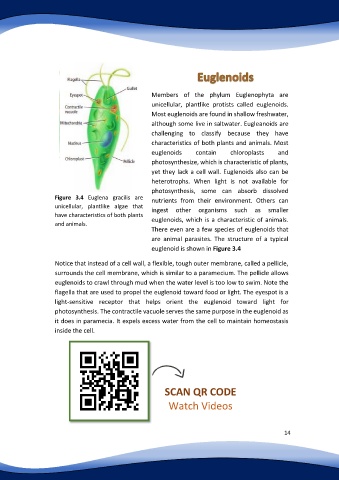
Figure 3.4 Euglena gracilis are
nutrients from their environment. Others can
unicellular, plantlike algae that
ingest other organisms such as smaller
have characteristics of both plants
and animals. euglenoids, which is a characteristic of animals.
There even are a few species of euglenoids that
are animal parasites. The structure of a typical
euglenoid is shown in Figure 3.4
Notice that instead of a cell wall, a flexible, tough outer membrane, called a pellicle,
surrounds the cell membrane, which is similar to a paramecium. The pellicle allows
euglenoids to crawl through mud when the water level is too low to swim. Note the
flagella that are used to propel the euglenoid toward food or light. The eyespot is a
light-sensitive receptor that helps orient the euglenoid toward light for
photosynthesis. The contractile vacuole serves the same purpose in the euglenoid as
it does in paramecia. It expels excess water from the cell to maintain homeostasis
inside the cell.
SCAN QR CODE
Watch Videos
14