Page 58 - 台灣肝癌醫學冬季會手冊-1222-V3_Neat
P. 58
69.2 % were male. Forty-four patients (56.4 %) experienced tumor progression with
time to progression 5.1 months (95% confidence interval (CI): 4.7-6.8) months. In
multivariate Cox regression analysis, albumin-bilirubin (ALBI) grade II (adjusted HR:
2.883, P=0.0104), and treatment duration less than three months (adjusted HR: 3.801,
P=0.0014) were the independent predictive factors for tumor progression. On the
other hand, patients achieving objective response under lenvatinib treatment was the
independent protective factor for tumor progression (adjusted HR: 0.144, P=0.0020).
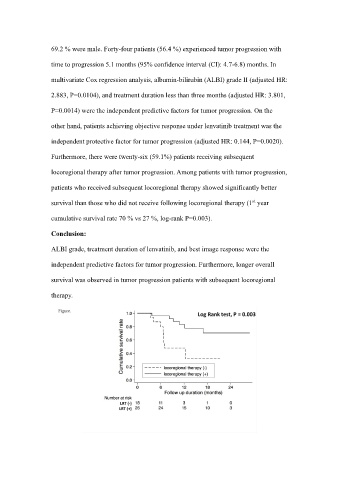
Furthermore, there were twenty-six (59.1%) patients receiving subsequent
locoregional therapy after tumor progression. Among patients with tumor progression,
patients who received subsequent locoregional therapy showed significantly better
st
survival than those who did not receive following locoregional therapy (1 year
cumulative survival rate 70 % vs 27 %, log-rank P=0.003).
Conclusion:
ALBI grade, treatment duration of lenvatinib, and best image response were the
independent predictive factors for tumor progression. Furthermore, longer overall
survival was observed in tumor progression patients with subsequent locoregional
therapy.