Page 166 - International Space Station Benefits for Humanity, 3rd edition.
P. 166
Experiment Module (JEM), where the samples are kept pathogen, and other enzymes in the DPP family,
for a period of 1 to 2 months at a stable temperature, the substance would become an antimicrobial agent.
20°C (68°F). A counter-diffusion method called the Thus, the research team also decided to develop
Gel-Tube method is used for crystallization whereby antimicrobial agents.
polyethylene glycol or salt solution is diffused into Several types of DPPs exist, and each one works
the protein solution, which is separated by a porous differently. For example, DAP BII (DPP7) recognizes
membrane inside a tube. In this method, concentration and cleaves hydrophobic or basic amino acids.
of polyethylene glycol in the protein solution gradually On the other hand, DPP11 recognizes acidic amino
increases and finally satisfies the condition for protein acids. These enzymes are not found in humans, they
crystallization. In addition to the existing experiments are only found in microorganisms. In other words, if you
conducted at 20°C (68°F), experiments at 4°C (40°F) can make medicines to suppress the function of these
are now being started. Crystallization at 4°C (40°F) enzymes, it is harmless for humans and only suppresses
realizes the crystallization of candidate drugs in high the growth of bacteria. If the peptide binding mode of
demand, such as unstable hydrosoluble proteins protein is clarified in detail, a new drug could be created
and membrane proteins.
that targets only DPP of microorganisms, but has no
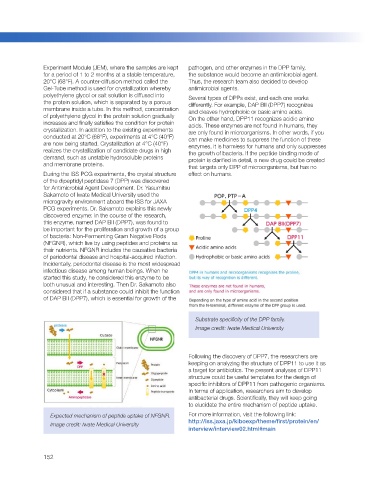
During the ISS PCG experiments, the crystal structure effect on humans.
of the dipeptidyl peptidase 7 (DPP) was discovered
for Antimicrobial Agent Development. Dr. Yasumitsu
Sakamoto of Iwate Medical University used the
microgravity environment aboard the ISS for JAXA
PCG experiments. Dr. Sakamoto explains this newly
discovered enzyme: In the course of the research,
this enzyme, named DAP BII (DPP7), was found to
be important for the proliferation and growth of a group
of bacteria: Non-Fermenting Gram Negative Rods
(NFGNR), which live by using peptides and proteins as
their nutrients. NFGNR includes the causative bacteria
of periodontal disease and hospital-acquired infection.
Incidentally, periodontal disease is the most widespread
infectious disease among human beings. When he
started this study, he considered this enzyme to be
both unusual and interesting. Then Dr. Sakamoto also
considered that if a substance could inhibit the function
of DAP BII (DPP7), which is essential for growth of the
Substrate specificity of the DPP family.
Image credit: Iwate Medical University
Following the discovery of DPP7, the researchers are
keeping on analyzing the structure of DPP11 to use it as
a target for antibiotics. The present analyses of DPP11
structure could be useful templates for the design of
specific inhibitors of DPP11 from pathogenic organisms.
In terms of application, researchers aim to develop
antibacterial drugs. Scientifically, they will keep going
to elucidate the entire mechanism of peptide uptake.
Expected mechanism of peptide uptake of NFGNR. For more information, visit the following link:
http://iss.jaxa.jp/kiboexp/theme/first/protein/en/
Image credit: Iwate Medical University
interview/interview02.html#main
152