Page 108 - BUKU JILID 2 ENGLISH FOR PROFESSIONAL NURSE FIX
P. 108
be placed on the baby's scalp to directly monitor the fetal heart rate. The clip is called a fetal scalp electrode
(FSE). The second measure is internal contraction monitoring. To gauge the strength of your contractions,
a small catheter (Intrauterine pressure catheter or IUPC) is placed in your uterus. Combined with an
internal fetal monitor, an IUPC will give a more precise reading of the baby's heart rate and your
contractions.
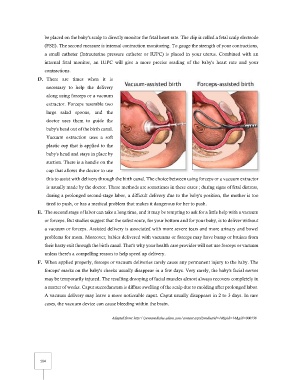
D. There are times when it is
necessary to help the delivery
along using forceps or a vacuum
extractor. Forceps resemble two
large salad spoons, and the
doctor uses them to guide the
baby's head out of the birth canal.
Vacuum extraction uses a soft
plastic cup that is applied to the
baby's head and stays in place by
suction. There is a handle on the
cup that allows the doctor to use
this to assist with delivery through the birth canal. The choice between using forceps or a vacuum extractor
is usually made by the doctor. These methods are sometimes in these cases ; during signs of fetal distress,
during a prolonged second-stage labor, a difficult delivery due to the baby's position, the mother is too
tired to push, or has a medical problem that makes it dangerous for her to push.
E. The second stage of labor can take a long time, and it may be tempting to ask for a little help with a vacuum
or forceps. But studies suggest that the safest route, for your bottom and for your baby, is to deliver without
a vacuum or forceps. Assisted delivery is associated with more severe tears and more urinary and bowel
problems for mom. Moreover, babies delivered with vacuums or forceps may have bump or bruises from
their hasty exit through the birth canal. That's why your health care provider will not use forceps or vacuum
unless there's a compelling reason to help speed up delivery.
F. When applied properly, forceps or vacuum deliveries rarely cause any permanent injury to the baby. The
forceps' marks on the baby's cheeks usually disappear in a few days. Very rarely, the baby's facial nerves
may be temporarily injured. The resulting drooping of facial muscles almost always recovers completely in
a matter of weeks. Caput succedaneum is diffuse swelling of the scalp due to molding after prolonged labor.
A vacuum delivery may leave a more noticeable caput. Caput usually disappears in 2 to 3 days. In rare
cases, the vacuum device can cause bleeding within the brain.
Adapted from: http://pennmedicine.adam.com/content.aspx?productid=14&pid=14&gid=000138
104