Page 136 - Demo 1
P. 136
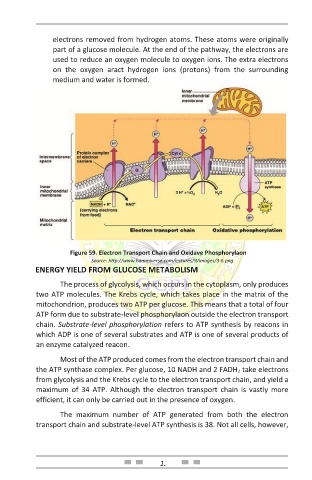
electrons removed from hydrogen atoms. These atoms were originally
part of a glucose molecule. At the end of the pathway, the electrons are
used to reduce an oxygen molecule to oxygen ions. The extra electrons
on the oxygen aract hydrogen ions (protons) from the surrounding
medium and water is formed.
Figure 59. Electron Transport Chain and Oxidave Phosphorylaon
Source: http://www.hammiverse.com/lectures/9/images/3-6.png
ENERGY YIELD FROM GLUCOSE METABOLISM
The process of glycolysis, which occurs in the cytoplasm, only produces
two ATP molecules. The Krebs cycle, which takes place in the matrix of the
mitochondrion, produces two ATP per glucose. This means that a total of four
ATP form due to substrate-level phosphorylaon outside the electron transport
chain. Substrate-level phosphorylation refers to ATP synthesis by reacons in
which ADP is one of several substrates and ATP is one of several products of
an enzyme catalyzed reacon.
Most of the ATP produced comes from the electron transport chain and
the ATP synthase complex. Per glucose, 10 NADH and 2 FADH2 take electrons
from glycolysis and the Krebs cycle to the electron transport chain, and yield a
maximum of 34 ATP. Although the electron transport chain is vastly more
efficient, it can only be carried out in the presence of oxygen.
The maximum number of ATP generated from both the electron
transport chain and substrate-level ATP synthesis is 38. Not all cells, however,
128