Page 15 - Demo 1
P. 15
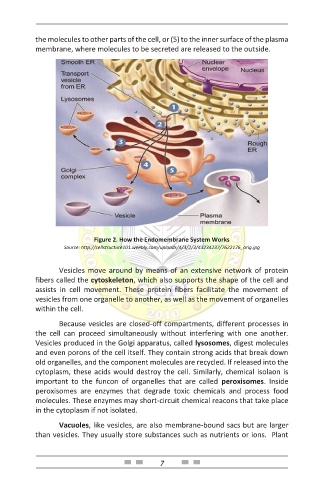
the molecules to other parts of the cell, or (5) to the inner surface of the plasma
membrane, where molecules to be secreted are released to the outside.
Figure 2. How the Endomembrane System Works
Source: http://cellstructure101.weebly.com/uploads/4/3/2/3/43234237/7622176_orig.jpg
Vesicles move around by means of an extensive network of protein
fibers called the cytoskeleton, which also supports the shape of the cell and
assists in cell movement. These protein fibers facilitate the movement of
vesicles from one organelle to another, as well as the movement of organelles
within the cell.
Because vesicles are closed-off compartments, different processes in
the cell can proceed simultaneously without interfering with one another.
Vesicles produced in the Golgi apparatus, called lysosomes, digest molecules
and even porons of the cell itself. They contain strong acids that break down
old organelles, and the component molecules are recycled. If released into the
cytoplasm, these acids would destroy the cell. Similarly, chemical isolaon is
important to the funcon of organelles that are called peroxisomes. Inside
peroxisomes are enzymes that degrade toxic chemicals and process food
molecules. These enzymes may short-circuit chemical reacons that take place
in the cytoplasm if not isolated.
Vacuoles, like vesicles, are also membrane-bound sacs but are larger
than vesicles. They usually store substances such as nutrients or ions. Plant
7