Page 99 - Demo 1
P. 99
with thymine. This pairing allows the two chains to remain intact, and is
especially important during DNA replicaon.
RNA (Ribonucleic Acid): Protein Synthesis
The other type of nucleic acid, RNA, is mostly involved in protein
synthesis. The DNA molecules never leave the nucleus, but instead use an RNA
intermediary to communicate with the rest of the cell. RNA is the molecule
that helps in transcribing and translang DNA into a protein. Other types of RNA
are also involved in protein synthesis and its regulaon.
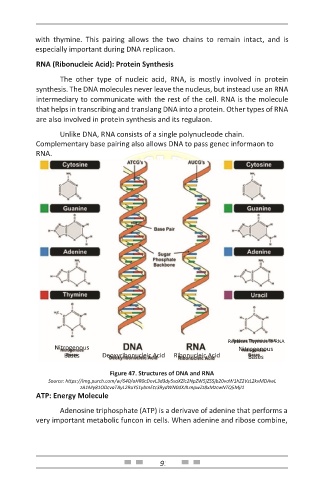
Unlike DNA, RNA consists of a single polynucleode chain.
Complementary base pairing also allows DNA to pass genec informaon to
RNA.
Figure 47. Structures of DNA and RNA
Source: https://img.purch.com/w/640/aHR0cDovL3d3dy5saXZlc2NpZW5jZS5jb20vaW1hZ2VzL2kvMDAwL
zA1My81ODcvaTAyL2RuYS1ybmEtc3RydWN0dXJlLmpwZz8xMzcwNTQ5MjI1
ATP: Energy Molecule
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a derivave of adenine that performs a
very important metabolic funcon in cells. When adenine and ribose combine,
91