Page 61 - REMOVABLE ORTHODONTIC APPLIANCES
P. 61
Class I malocclusions 53
as a button or a short length of stainless steel
wire bent into a hook. The patient must be able
to engage the buccal spring onto the hook. An
alternative approach is to use a latex elastic
which engages the hook on the canine and is
supported by a buccal arm with a fish tail which
controls the direction of the elastic force.
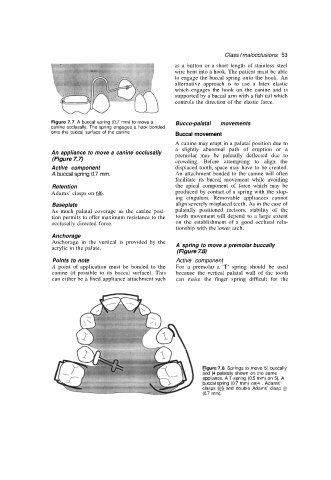
Figure 7.7 A buccal spring (0.7 mm) to move a Bucco-palatal movements
canine occlusally. The spring engages a hook bonded
onto the buccal surface of the canine.
Buccal movement
A canine may erupt in a palatal position due to
a slightly abnormal path of eruption or a
An appliance to move a canine occlusally premolar may be palatally deflected due to
(Figure 7.7)
crowding. Before attempting to align the
Active component displaced tooth, space may have to be created.
A buccal spring 0.7 mm. An attachment bonded to the canine will often
facilitate its buccal movement while avoiding
Retention the apical component of force which may be
Adams' clasps on 6|6. produced by contact of a spring with the slop-
ing cingulum. Removable appliances cannot
Baseplate align severely misplaced teeth. As in the case of
As much palatal coverage as the canine posi- palatally positioned incisors, stability of the
tion permits to offer maximum resistance to the tooth movement will depend to a large extent
occlusally directed force. on the establishment of a good occlusal rela-
tionship with the lower arch.
Anchorage
Anchorage in the vertical is provided by the A spring to move a premolar buccally
acrylic in the palate.
(Figure 7.8)
Points to note Active component
A point of application must be bonded to the For a premolar a 'T' spring should be used
canine (if possible to its buccal surface). This because the vertical palatal wall of the tooth
can either be a fixed appliance attachment such can make the finger spring difficult for the
Figure 7.8 Springs to move 5| buccally
and |4 palatally shown on the same
appliance. A T-spring (0.5 mm) on 5|. A
buccal spring (0.7 mm) on|4 . Adams'
clasps 6|6 and double Adams' clasp l|l
(0.7 mm).