Page 190 - Volume 2_CHANGES_merged_with links
P. 190
Obstacles to progress
Realities
high interest rates,the debt increased to US$ 1419 billion in 1992 – despite the repayments!
The rising interest rates forced developing countries to take out new loans to avoid bankruptcy.
"How The IMF-World Bank and Structural Adjustment Program(SAP) Destroyed Africa." 221
Newsrescuemedia (May 2009)
*****
Debt-to-GDP ratio and default probability
“ For external debt, "safe" thresholds for highly debt intolerant emerging markets appear to be
surprisingly low, perhaps as low as 15 to 20 percent of GNP in many cases, and these
thresholds depend heavily on the country's record of default and inflation “
"Debt Intolerance" 222
Reinhart, C. M.; Rogoff, K. S.; Savastano, M. A. (2003)
*****
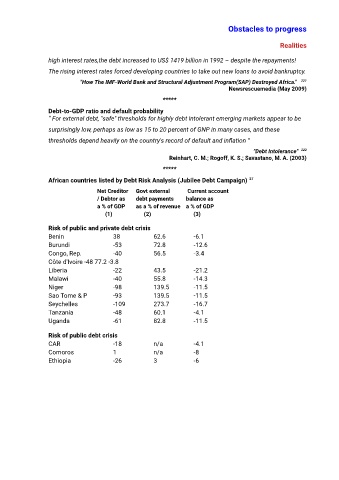
African countries listed by Debt Risk Analysis (Jubilee Debt Campaign) 27
Net Creditor Govt external Current account
/ Debtor as debt payments balance as
a % of GDP as a % of revenue a % of GDP
(1) (2) (3)
Risk of public and private debt crisis
Benin 38 62.6 -6.1
Burundi -53 72.8 -12.6
Congo, Rep. -40 56.5 -3.4
Côte d'Ivoire -48 77.2 -3.8
Liberia -22 43.5 -21.2
Malawi -40 55.8 -14.3
Niger -98 139.5 -11.5
Sao Tome & P -93 139.5 -11.5
Seychelles -109 273.7 -16.7
Tanzania -48 60.1 -4.1
Uganda -61 82.8 -11.5
Risk of public debt crisis
CAR -18 n/a -4.1
Comoros 1 n/a -8
Ethiopia -26 3 -6