Page 20 - (1-1)eng
P. 20
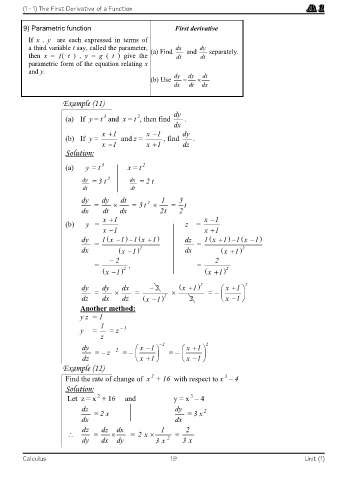
(1 - 1) The First Derivative of a Function
9) Parametric function First derivative
If x , y are each expressed in terms of
a third variable t say, called the parameter, (a) Find dx and dy separately.
then x = ƒ( t ) , y = g ( t ) give the dt dt
parametric form of the equation relating x
and y. dy dy dt
(b) Use
dx dt dx
Example (11)
3
2
(a) If y = t and x = t , then find dy .
dx
x 1 x 1 dy
(b) If y = and z = , find .
x 1 x 1 dz
Solution:
3
2
(a) y = t x = t
2
dy = 3 t dx = 2 t
dt dt
dy dy dt 1 3
2
= = 3 t = t
dx dt dx 2t 2
x 1 x 1
(b) y = z =
x 1 x 1
dy 1 x 1 1 x 1 dz 1 x 1 1 x 1
= =
dx x 1 2 dx x 1 2
2 2
= , =
x 1 2 x 1 2
dy dy dx 2 x 1 2 x 1 2
= = = –
dz dx dz x 1 2 2 x 1
Another method:
y z = 1
1
y = = z – 1
z
dy x 1 2 x 1 2
– 2
= – z = – = –
dz x 1 x 1
Example (12)
3
2
Find the rate of change of x + 16 with respect to x – 4
Solution:
2
3
Let z = x + 16 and y = x – 4
dz dy
2
= 2 x = 3 x
dx dx
dz dz dx 1 2
= = 2 x =
dy dx dy 3 x 2 3 x
Calculus 19 Unit (1)