Page 138 - Clinical Manual of Small Animal Endosurgery
P. 138
126 Clinical Manual of Small Animal Endosurgery
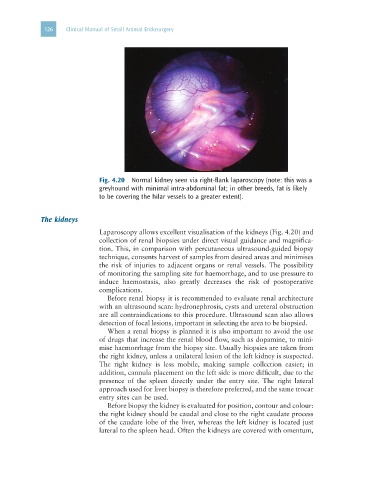
Fig. 4.20 Normal kidney seen via right-flank laparoscopy (note: this was a
greyhound with minimal intra-abdominal fat; in other breeds, fat is likely
to be covering the hilar vessels to a greater extent).
The kidneys
Laparoscopy allows excellent visualisation of the kidneys (Fig. 4.20) and
collection of renal biopsies under direct visual guidance and magnifica-
tion. This, in comparison with percutaneous ultrasound-guided biopsy
technique, consents harvest of samples from desired areas and minimises
the risk of injuries to adjacent organs or renal vessels. The possibility
of monitoring the sampling site for haemorrhage, and to use pressure to
induce haemostasis, also greatly decreases the risk of postoperative
complications.
Before renal biopsy it is recommended to evaluate renal architecture
with an ultrasound scan: hydronephrosis, cysts and ureteral obstruction
are all contraindications to this procedure. Ultrasound scan also allows
detection of focal lesions, important in selecting the area to be biopsied.
When a renal biopsy is planned it is also important to avoid the use
of drugs that increase the renal blood flow, such as dopamine, to mini-
mise haemorrhage from the biopsy site. Usually biopsies are taken from
the right kidney, unless a unilateral lesion of the left kidney is suspected.
The right kidney is less mobile, making sample collection easier; in
addition, cannula placement on the left side is more difficult, due to the
presence of the spleen directly under the entry site. The right lateral
approach used for liver biopsy is therefore preferred, and the same trocar
entry sites can be used.
Before biopsy the kidney is evaluated for position, contour and colour:
the right kidney should be caudal and close to the right caudate process
of the caudate lobe of the liver, whereas the left kidney is located just
lateral to the spleen head. Often the kidneys are covered with omentum,