Page 152 - Differential Diagnosis in Small Animal Cytology, The Skin and Subcutis
P. 152
Mesenchymal Tumours and Other Neoplasms
139
Differential diagnosis
VetBooks.ir Subcutaneous adipose tissue (accidental aspiration)
Pearls and Pitfalls
Aspirates from lipoma often contain variable amounts of lipid material. Slides often do
not dry and have an oily appearance. The lipid component may dissolve during fixation in
methanol-based fixatives and may detach the adipocytes from the slide, leaving an acellular
smear. This can be prevented by: (i) heat fixation (unstained slide passed through a flame for
a few seconds); (ii) using poly-l-lysine slides.
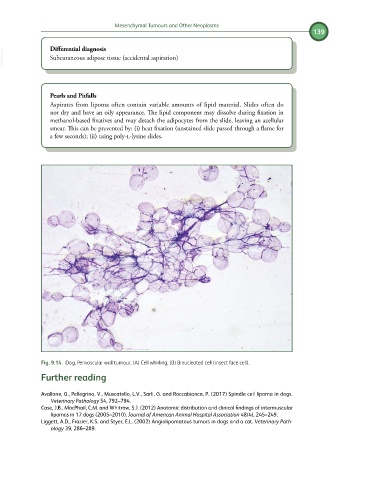
Fig. 9.14. Dog. Perivascular wall tumour. (A) Cell whirling. (B) Binucleated cell (insect face cell).
Further reading
Avallone, G., Pellegrino, V., Muscatello, L.V., Sarli, G. and Roccabianca, P. (2017) Spindle cell lipoma in dogs.
Veterinary Pathology 54, 792–794.
Case, J.B., MacPhail, C.M. and Whitrow, S.J. (2012) Anatomic distribution and clinical findings of intermuscular
lipomas in 17 dogs (2005–2010). Journal of American Animal Hospital Association 48(4), 245–249.
Liggett, A.D., Frazier, K.S. and Styer, E.L. (2002) Angiolipomatous tumors in dogs and a cat. Veterinary Path-
ology 39, 286–289.