Page 99 - Rapid Review of ECG Interpretation in Small Animal Practice, 2nd Edition
P. 99
Answer 32 ECG Cases
Answer 32
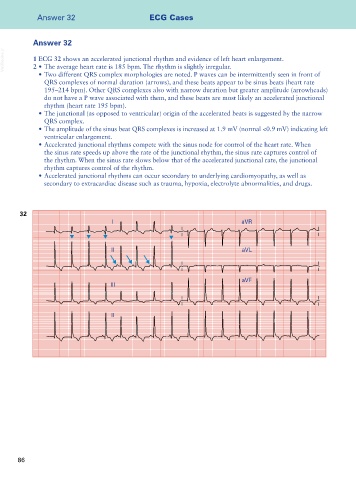
VetBooks.ir 1 ECG 32 shows an accelerated junctional rhythm and evidence of left heart enlargement.
2 • The average heart rate is 185 bpm. The rhythm is slightly irregular.
• Two different QRS complex morphologies are noted. P waves can be intermittently seen in front of
QRS complexes of normal duration (arrows), and these beats appear to be sinus beats (heart rate
195–214 bpm). Other QRS complexes also with narrow duration but greater amplitude (arrowheads)
do not have a P wave associated with them, and these beats are most likely an accelerated junctional
rhythm (heart rate 195 bpm).
• The junctional (as opposed to ventricular) origin of the accelerated beats is suggested by the narrow
QRS complex.
• The amplitude of the sinus beat QRS complexes is increased at 1.9 mV (normal <0.9 mV) indicating left
ventricular enlargement.
• Accelerated junctional rhythms compete with the sinus node for control of the heart rate. When
the sinus rate speeds up above the rate of the junctional rhythm, the sinus rate captures control of
the rhythm. When the sinus rate slows below that of the accelerated junctional rate, the junctional
rhythm captures control of the rhythm.
• Accelerated junctional rhythms can occur secondary to underlying cardiomyopathy, as well as
secondary to extracardiac disease such as trauma, hypoxia, electrolyte abnormalities, and drugs.
32
I aVR
II aVL
aVF
III
II
86