Page 451 - The Toxicology of Fishes
P. 451
Toxic Responses of the Fish Nervous System 431
O
(CH 3) 2CHO CH 3O O
P F P
(CH 3) 2CHO CH 3C N SCH 3
O H
DFP ACEPHATE
S O
C 2H 5O C 2H 5O
PO NO 2 PO NO 2
C 2H 5O C 2H 5O
PARATHION PARAOXON
O CH 3 O
CH 3O S
P O CH CHCOCH 3 C 2H 5O
P S CH 2 S CH 2CH 3
CH 3O C 2H 5O
MEVINPHOS PHORATE
C 2H 5O S
P C 2H 5O S
O NO 2 P
C 2H 5 S
EPN DYFONATE
S CI
C 2H 5O N CH(CH 3) 2
P O S N
C 2H 5O C 2H 5O
N P O CI
C 2H 5O
CH 3
CI
DIAZINON CHLORPYRIFOS
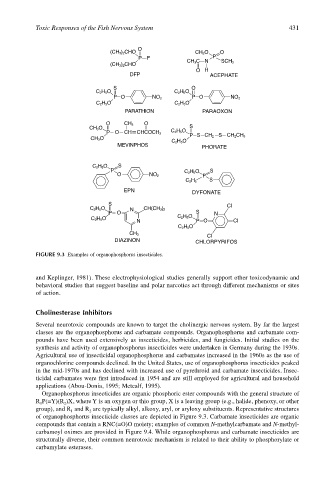
FIGURE 9.3 Examples of organophosphorus insecticides.
and Keplinger, 1981). These electrophysiological studies generally support other toxicodynamic and
behavioral studies that suggest baseline and polar narcotics act through different mechanisms or sites
of action.
Cholinesterase Inhibitors
Several neurotoxic compounds are known to target the cholinergic nervous system. By far the largest
classes are the organophosphorus and carbamate compounds. Organophosphorus and carbamate com-
pounds have been used extensively as insecticides, herbicides, and fungicides. Initial studies on the
synthesis and activity of organophosphorus insecticides were undertaken in Germany during the 1930s.
Agricultural use of insecticidal organophosphorus and carbamates increased in the 1960s as the use of
organochlorine compounds declined. In the United States, use of organophosphorus insecticides peaked
in the mid-1970s and has declined with increased use of pyrethroid and carbamate insecticides. Insec-
ticidal carbamates were first introduced in 1954 and are still employed for agricultural and household
applications (Abou-Donia, 1995; Metcalf, 1995).
Organophosphorus insecticides are organic phosphoric ester compounds with the general structure of
R P(=Y)(R )X, where Y is an oxygen or thio group, X is a leaving group (e.g., halide, phenoxy, or other
1
2
group), and R and R are typically alkyl, alkoxy, aryl, or aryloxy substituents. Representative structures
1
2
of organophosphorus insecticide classes are depicted in Figure 9.3. Carbamate insecticides are organic
compounds that contain a RNC(=O)O moiety; examples of common N-methylcarbamate and N-methyl-
carbamoyl oximes are provided in Figure 9.4. While organophosphorus and carbamate insecticides are
structurally diverse, their common neurotoxic mechanism is related to their ability to phosphorylate or
carbamylate esterases.