Page 47 - Feline Cardiology
P. 47
Chapter 6: Radiography 41
T4 5
L - 4.5v
S - 3.0v
T
VHS - 7.5v Diagnostic Testing
S
L
D
7
A
LA
L
R S
A
LV
RV
B C
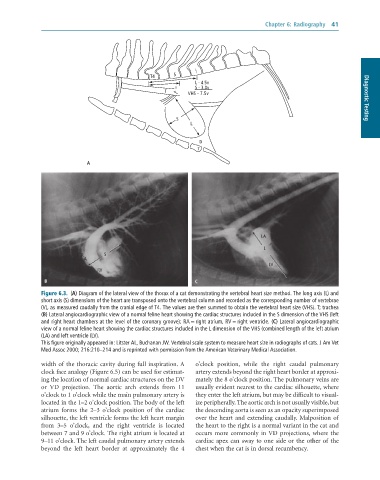
Figure 6.3. (A) Diagram of the lateral view of the thorax of a cat demonstrating the vertebral heart size method. The long axis (L) and
short axis (S) dimensions of the heart are transposed onto the vertebral column and recorded as the corresponding number of vertebrae
(V), as measured caudally from the cranial edge of T4. The values are then summed to obtain the vertebral heart size (VHS). T; trachea
(B) Lateral angiocardiographic view of a normal feline heart showing the cardiac structures included in the S dimension of the VHS (left
and right heart chambers at the level of the coronary groove); RA = right atrium, RV = right ventricle. (C) Lateral angiocardiographic
view of a normal feline heart showing the cardiac structures included in the L dimension of the VHS (combined length of the left atrium
(LA) and left ventricle (LV).
This figure originally appeared in: Litster AL, Buchanan JW. Vertebral scale system to measure heart size in radiographs of cats. J Am Vet
Med Assoc 2000; 216:210–214 and is reprinted with permission from the American Veterinary Medical Association.
width of the thoracic cavity during full inspiration. A o’clock position, while the right caudal pulmonary
clock face analogy (Figure 6.5) can be used for estimat- artery extends beyond the right heart border at approxi-
ing the location of normal cardiac structures on the DV mately the 8 o’clock position. The pulmonary veins are
or VD projection. The aortic arch extends from 11 usually evident nearest to the cardiac silhouette, where
o’clock to 1 o’clock while the main pulmonary artery is they enter the left atrium, but may be difficult to visual-
located in the 1–2 o’clock position. The body of the left ize peripherally. The aortic arch is not usually visible, but
atrium forms the 2–3 o’clock position of the cardiac the descending aorta is seen as an opacity superimposed
silhouette, the left ventricle forms the left heart margin over the heart and extending caudally. Malposition of
from 3–5 o’clock, and the right ventricle is located the heart to the right is a normal variant in the cat and
between 7 and 9 o’clock. The right atrium is located at occurs more commonly in VD projections, where the
9–11 o’clock. The left caudal pulmonary artery extends cardiac apex can sway to one side or the other of the
beyond the left heart border at approximately the 4 chest when the cat is in dorsal recumbency.