Page 1220 - Veterinary Toxicology, Basic and Clinical Principles, 3rd Edition
P. 1220
Prevention and Treatment of Poisoning Chapter | 82 1151
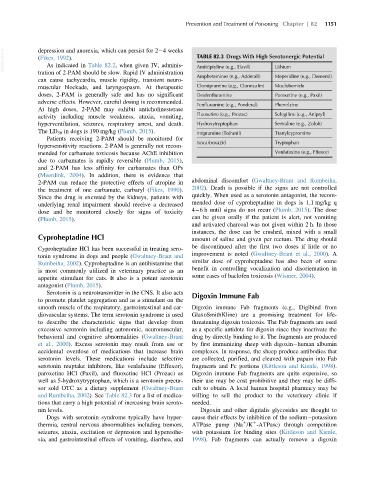
VetBooks.ir depression and anorexia, which can persist for 2 4 weeks TABLE 82.3 Drugs With High Serotonergic Potential
(Fikes, 1992).
As indicated in Table 82.2, when given IV, adminis-
tration of 2-PAM should be slow. Rapid IV administration Amitriptyline (e.g., Elavil) Lithium
Amphetamines (e.g., Adderall) Meperidine (e.g., Demerol)
can cause tachycardia, muscle rigidity, transient neuro-
muscular blockade, and laryngospasm. At therapeutic Clomipramine (e.g., Clomicalm) Moclobemide
doses, 2-PAM is generally safe and has no significant Dexfenfluramine Paroxetine (e.g., Paxil)
adverse effects. However, careful dosing is recommended.
Fenfluramine (e.g., Ponderal) Phenelzine
At high doses, 2-PAM may exhibit anticholinesterase
activity including muscle weakness, ataxia, vomiting, Fluoxetine (e.g., Prozac) Selegiline (e.g., Anipryl)
hyperventilation, seizures, respiratory arrest, and death. Hydroxytryptophan Sertraline (e.g., Zoloft)
The LD 50 in dogs is 190 mg/kg (Plumb, 2015). Imipramine (Tofranil) Tranylcypromine
Patients receiving 2-PAM should be monitored for
Isocarboxazid Tryptophan
hypersensitivity reactions. 2-PAM is generally not recom-
mended for carbamate toxicosis because AChE inhibition Venlafaxine (e.g., Effexor)
due to carbamates is rapidly reversible (Plumb, 2015),
and 2-PAM has less affinity for carbamates than OPs
(Meerdink, 2004). In addition, there is evidence that
2-PAM can reduce the protective effects of atropine in abdominal discomfort (Gwaltney-Brant and Rumbeiha,
the treatment of one carbamate, carbaryl (Fikes, 1990). 2002). Death is possible if the signs are not controlled
Since the drug is excreted by the kidneys, patients with quickly. When used as a serotonin antagonist, the recom-
underlying renal impairment should receive a decreased mended dose of cyproheptadine in dogs is 1.1 mg/kg q
dose and be monitored closely for signs of toxicity 4 6 h until signs do not recur (Plumb, 2015). The dose
can be given orally if the patient is alert, not vomiting
(Plumb, 2015).
and activated charcoal was not given within 2 h. In those
instances, the dose can be crushed, mixed with a small
Cyproheptadine HCl amount of saline and given per rectum. The drug should
be discontinued after the first two doses if little or no
Cyproheptadine HCl has been successful in treating sero-
improvement is noted (Gwaltney-Brant et al., 2000). A
tonin syndrome in dogs and people (Gwaltney-Brant and
similar dose of cyproheptadine has also been of some
Rumbeiha, 2002). Cyproheptadine is an antihistamine that
benefit in controlling vocalization and disorientation in
is most commonly utilized in veterinary practice as an
some cases of baclofen toxicosis (Wismer, 2004).
appetite stimulant for cats. It also is a potent serotonin
antagonist (Plumb, 2015).
Serotonin is a neurotransmitter in the CNS. It also acts Digoxin Immune Fab
to promote platelet aggregation and as a stimulant on the
smooth muscle of the respiratory, gastrointestinal and car- Digoxin immune Fab fragments (e.g., Digibind from
diovascular systems. The term serotonin syndrome is used GlaxoSmithKline) are a promising treatment for life-
to describe the characteristic signs that develop from threatening digoxin toxicosis. The Fab fragments are used
excessive serotonin including autonomic, neuromuscular, as a specific antidote for digoxin since they inactivate the
behavioral and cognitive abnormalities (Gwaltney-Brant drug by directly binding to it. The fragments are produced
et al., 2000). Excess serotonin may result from use or by first immunizing sheep with digoxin human albumin
accidental overdose of medications that increase brain complexes. In response, the sheep produce antibodies that
serotonin levels. These medications include selective are collected, purified, and cleaved with papain into Fab
serotonin reuptake inhibitors, like venlafaxine (Effexor), fragments and Fc portions (Kittleson and Kienle, 1998).
paroxetine HCl (Paxil), and fluoxetine HCl (Prozac) as Digoxin immune Fab fragments are quite expensive, so
well as 5-hydroxytryptophan, which is a serotonin precur- their use may be cost prohibitive and they may be diffi-
sor sold OTC as a dietary supplement (Gwaltney-Brant cult to obtain. A local human hospital pharmacy may be
and Rumbeiha, 2002). See Table 82.3 for a list of medica- willing to sell the product to the veterinary clinic if
tions that carry a high potential of increasing brain seroto- needed.
nin levels. Digoxin and other digitalis glycosides are thought to
Dogs with serotonin syndrome typically have hyper- cause their effects by inhibition of the sodium potassium
1 1
thermia, central nervous abnormalities including tremors, ATPase pump (Na /K -ATPase) through competition
seizures, ataxia, excitation or depression and hyperesthe- with potassium for binding sites (Kittleson and Kienle,
sia, and gastrointestinal effects of vomiting, diarrhea, and 1998). Fab fragments can actually remove a digoxin