Page 95 - Veterinary Toxicology, Basic and Clinical Principles, 3rd Edition
P. 95
62 SECTION | I General
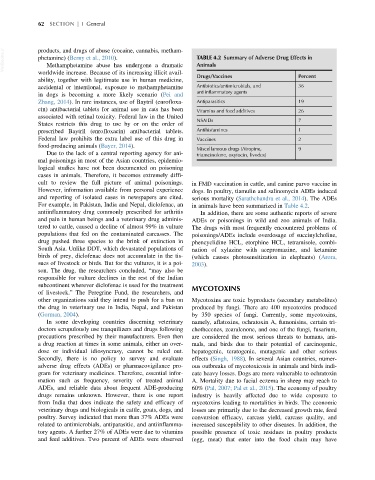
VetBooks.ir products, and drugs of abuse (cocaine, cannabis, metham- TABLE 4.2 Summary of Adverse Drug Effects in
phetamine) (Berny et al., 2010).
Animals
Methamphetamine abuse has undergone a dramatic
worldwide increase. Because of its increasing illicit avail-
Drugs/Vaccines Percent
ability, together with legitimate use in human medicine,
accidental or intentional, exposure to methamphetamine Antibiotics/antimicrobials, and 36
antiinflammatory agents
in dogs is becoming a more likely scenario (Pei and
Zhang, 2014). In rare instances, use of Baytril (enrofloxa- Antiparasitics 19
cin) antibacterial tablets for animal use in cats has been Vitamins and feed additives 26
associated with retinal toxicity. Federal law in the United
NSAIDs 7
States restricts this drug to use by or on the order of
prescribed Baytril (enrofloxacin) antibacterial tablets. Antihistamines 1
Federal law prohibits the extra label use of this drug in Vaccines 2
food-producing animals (Bayer, 2014).
Miscellaneous drugs (Atropine, 9
Due to the lack of a central reporting agency for ani- triamcinolone, oxytocin, livodex)
mal poisonings in most of the Asian countries, epidemio-
logical studies have not been documented on poisoning
cases in animals. Therefore, it becomes extremely diffi-
cult to review the full picture of animal poisonings. in FMD vaccination in cattle, and canine parvo vaccine in
However, information available from personal experience dogs. In poultry, tiamulin and salinomycin ADEs induced
and reporting of isolated cases in newspapers are cited. serious mortality (Sarathchandra et al., 2014). The ADEs
For example, in Pakistan, India and Nepal, diclofenac, an in animals have been summarized in Table 4.2.
antiinflammatory drug commonly prescribed for arthritis In addition, there are some authentic reports of severe
and pain in human beings and a veterinary drug adminis- ADEs or poisonings in wild and zoo animals of India.
tered to cattle, caused a decline of almost 99% in vulture The drugs with most frequently encountered problems of
populations that fed on the contaminated carcasses. The poisonings/ADEs include overdosage of succinylcholine,
drug pushed three species to the brink of extinction in phencyclidine HCL, etorphine HCL, tetramisole, combi-
South Asia. Unlike DDT, which devastated populations of nation of xylazine with acepromazine, and ketamine
birds of prey, diclofenac does not accumulate in the tis- (which causes photosensitization in elephants) (Arora,
sues of livestock or birds. But for the vultures, it is a poi- 2003).
son. The drug, the researchers concluded, “may also be
responsible for vulture declines in the rest of the Indian
subcontinent wherever diclofenac is used for the treatment MYCOTOXINS
of livestock.” The Peregrine Fund, the researchers, and
other organizations said they intend to push for a ban on Mycotoxins are toxic byproducts (secondary metabolites)
the drug in veterinary use in India, Nepal, and Pakistan produced by fungi. There are 400 mycotoxins produced
(Gorman, 2004). by 350 species of fungi. Currently, some mycotoxins,
In some developing countries discerning veterinary namely, aflatoxins, ochratoxin A, fumonisins, certain tri-
doctors scrupulously use tranquilizers and drugs following chothecenes, zearalenone, and one of the fungi, fusarium,
precautions prescribed by their manufacturers. Even then are considered the most serious threats to humans, ani-
a drug reaction at times in some animals, either an over- mals, and birds due to their potential of carcinogenic,
dose or individual idiosyncrasy, cannot be ruled out. hepatogenic, teratogenic, mutagenic and other serious
Secondly, there is no policy to survey and evaluate effects (Singh, 1988). In several Asian countries, numer-
adverse drug effects (ADEs) or pharmacovigilance pro- ous outbreaks of mycotoxicosis in animals and birds indi-
gram for veterinary medicines. Therefore, essential infor- cate heavy losses. Dogs are more vulnerable to ochratoxin
mation such as frequency, severity of treated animal A. Mortality due to facial eczema in sheep may reach to
ADEs, and reliable data about frequent ADE-producing 60% (Pal, 2007; Pal et al., 2015). The economy of poultry
drugs remains unknown. However, there is one report industry is heavily affected due to wide exposure to
from India that does indicate the safety and efficacy of mycotoxins leading to mortalities in birds. The economic
veterinary drugs and biologicals in cattle, goats, dogs, and losses are primarily due to the decreased growth rate, feed
poultry. Survey indicated that more than 37% ADEs were conversion efficacy, carcass yield, carcass quality, and
related to antimicrobials, antiparasitic, and antiinflamma- increased susceptibility to other diseases. In addition, the
tory agents. A further 27% of ADEs were due to vitamins possible presence of toxic residues in poultry products
and feed additives. Two percent of ADEs were observed (egg, meat) that enter into the food chain may have