Page 474 - Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals, 8th Edition
P. 474
Physiology of Male Reproduction / 459
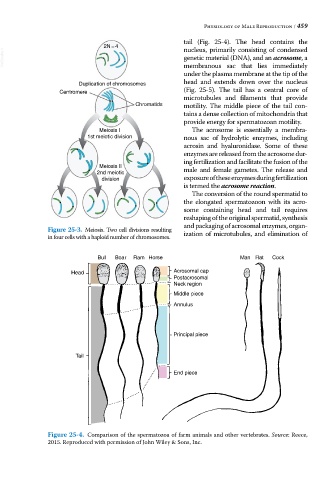
tail (Fig. 25‐4). The head contains the
2N=4 nucleus, primarily consisting of condensed
VetBooks.ir genetic material (DNA), and an acrosome, a
membranous sac that lies immediately
under the plasma membrane at the tip of the
Duplication of chromosomes head and extends down over the nucleus
Centromere (Fig. 25‐5). The tail has a central core of
microtubules and filaments that provide
Chromatids motility. The middle piece of the tail con-
tains a dense collection of mitochondria that
provide energy for spermatozoan motility.
Meiosis I The acrosome is essentially a membra-
1st meiotic division nous sac of hydrolytic enzymes, including
acrosin and hyaluronidase. Some of these
enzymes are released from the acrosome dur-
ing fertilization and facilitate the fusion of the
Meiosis II
2nd meiotic male and female gametes. The release and
division exposure of these enzymes during fertilization
is termed the acrosome reaction.
The conversion of the round spermatid to
the elongated spermatozoon with its acro-
some containing head and tail requires
reshaping of the original spermatid, synthesis
and packaging of acrosomal enzymes, organ-
Figure 25-3. Meiosis. Two cell divisions resulting
in four cells with a haploid number of chromosomes. ization of microtubules, and elimination of
Bull Boar Ram Horse Man Rat Cock
Head Acrosomal cap
Postacrosomal
Neck region
Middle piece
Annulus
Principal piece
Tail
End piece
Figure 25-4. Comparison of the spermatozoa of farm animals and other vertebrates. Source: Reece,
2015. Reproduced with permission of John Wiley & Sons, Inc.