Page 296 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 296
control virus infections, cytotoxic T cells must be able to recognize
VetBooks.ir any viral proteins expressed on the surface of infected cells. T cells
can indeed recognize and respond to these endogenous antigens,
but only if they are processed and bound to MHC class I molecules
(Chapter 11).
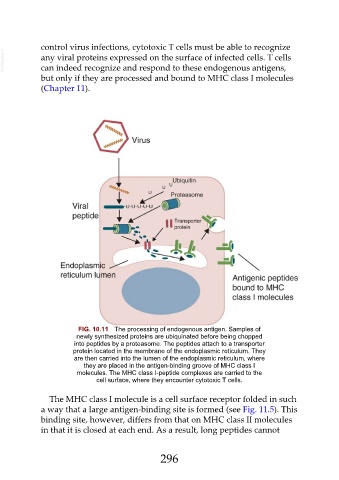
FIG. 10.11 The processing of endogenous antigen. Samples of
newly synthesized proteins are ubiquinated before being chopped
into peptides by a proteasome. The peptides attach to a transporter
protein located in the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum. They
are then carried into the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum, where
they are placed in the antigen-binding groove of MHC class I
molecules. The MHC class I-peptide complexes are carried to the
cell surface, where they encounter cytotoxic T cells.
The MHC class I molecule is a cell surface receptor folded in such
a way that a large antigen-binding site is formed (see Fig. 11.5). This
binding site, however, differs from that on MHC class II molecules
in that it is closed at each end. As a result, long peptides cannot
296