Page 303 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 303
the major histocompatibility complex (MHC). The receptors are
VetBooks.ir therefore called MHC molecules. Antigens can only trigger an
adaptive immune response after binding to MHC molecules. These
antigen-MHC complexes are then presented to T cell antigen
receptors and trigger a response. Since each MHC molecule acts as
an antigen receptor, the genes encoding them effectively determine
which antigens can or cannot trigger adaptive immunity. Thus the
MHC can be considered a cluster of genes that control antigen
presentation and so determine resistance to infectious diseases. The
ability of pathogens to evade, escape, or subvert immune defenses
places strong selection pressures on MHC genes and results in their
rapid evolution.
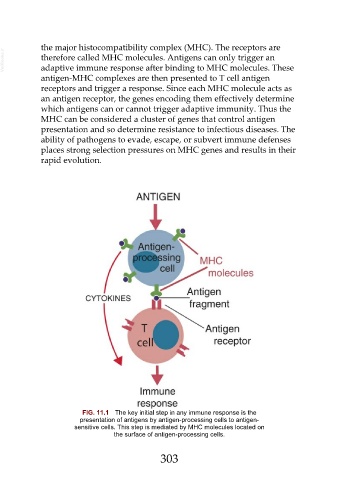
FIG. 11.1 The key initial step in any immune response is the
presentation of antigens by antigen-processing cells to antigen-
sensitive cells. This step is mediated by MHC molecules located on
the surface of antigen-processing cells.
303