Page 80 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 80
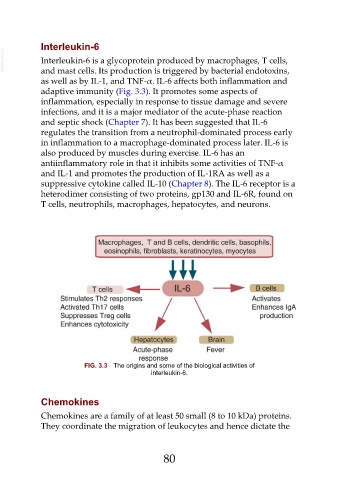
Interleukin-6
VetBooks.ir Interleukin-6 is a glycoprotein produced by macrophages, T cells,
and mast cells. Its production is triggered by bacterial endotoxins,
as well as by IL-1, and TNF-α. IL-6 affects both inflammation and
adaptive immunity (Fig. 3.3). It promotes some aspects of
inflammation, especially in response to tissue damage and severe
infections, and it is a major mediator of the acute-phase reaction
and septic shock (Chapter 7). It has been suggested that IL-6
regulates the transition from a neutrophil-dominated process early
in inflammation to a macrophage-dominated process later. IL-6 is
also produced by muscles during exercise. IL-6 has an
antiinflammatory role in that it inhibits some activities of TNF-α
and IL-1 and promotes the production of IL-1RA as well as a
suppressive cytokine called IL-10 (Chapter 8). The IL-6 receptor is a
heterodimer consisting of two proteins, gp130 and IL-6R, found on
T cells, neutrophils, macrophages, hepatocytes, and neurons.
FIG. 3.3 The origins and some of the biological activities of
interleukin-6.
Chemokines
Chemokines are a family of at least 50 small (8 to 10 kDa) proteins.
They coordinate the migration of leukocytes and hence dictate the
80