Page 858 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 858
VetBooks.ir
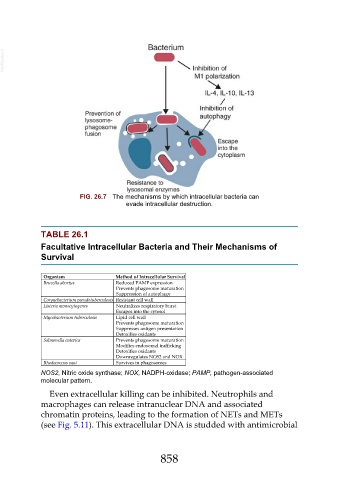
FIG. 26.7 The mechanisms by which intracellular bacteria can
evade intracellular destruction.
TABLE 26.1
Facultative Intracellular Bacteria and Their Mechanisms of
Survival
Organism Method of Intracellular Survival
Brucella abortus Reduced PAMP expression
Prevents phagosome maturation
Suppression of autophagy
Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis Resistant cell wall
Listeria monocytogenes Neutralizes respiratory burst
Escapes into the cytosol
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Lipid cell wall
Prevents phagosome maturation
Suppresses antigen presentation
Detoxifies oxidants
Salmonella enterica Prevents phagosome maturation
Modifies endosomal trafficking
Detoxifies oxidants
Downregulates NOS2 and NOX
Rhodococcus equi Survives in phagosomes
NOS2, Nitric oxide synthase; NOX, NADPH-oxidase; PAMP, pathogen-associated
molecular pattern.
Even extracellular killing can be inhibited. Neutrophils and
macrophages can release intranuclear DNA and associated
chromatin proteins, leading to the formation of NETs and METs
(see Fig. 5.11). This extracellular DNA is studded with antimicrobial
858