Page 524 - The Veterinary Laboratory and Field Manual 3rd Edition
P. 524
Arthropod vectors and arthropod-borne diseases 461
Pathogen distribution Mosquito species Vertebrate hosts diagnostic
methods
LaCrosse North America Ochlerotatus Chipmunks,
triseriatus squirrels, rodents
Ochlerotatus
canadensis
Snowshoe hare North America Ochlerotatus Lagomorphs
stimulans
Ochlerotatus
canadensis
Culiseta inornata
Tahyna Europe, west Asia Ochlerotatus Hares, pigs
caspius
Aedes vexans
Culiseta annulata
Rocio Brazil Ochlerotatus
scapularis
Caribbean Psorophora ferox
Note: For the most up to date guidelines on testing for specific diseases in livestock species check the online edition of the OIE
Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals http://www.oie.int/standard-setting/terrestrial-manual/access-
online/.
bait. Furthermore, additional attractants such as individuals that are flying/feeding at a specific
octenol can be used alongside carbon dioxide. time. Malaise traps are larger, tent-like structures
These trapping techniques target mostly blood- that funnel insects and collect them in a vessel
seeking females. Alternatives are gravid traps, at the highest point.
which selectively collect resting gravid females Because mosquitoes need standing water for
after a blood meal, and aspiration from the envi- their larval and pupal development, a trap loca-
ronment or the host, which is less biased for tion in the vicinity of an open, organically rich
gender of the mosquito, but selectively collects water source promises the highest catch rates.
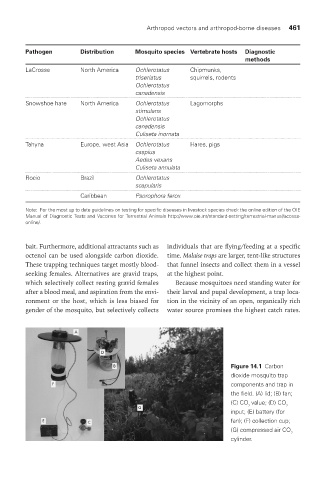
Figure 14.1 Carbon
dioxide mosquito trap
components and trap in
the field. (A) lid; (B) fan;
(C) CO value; (D) CO
2 2
input; (E) battery (for
fan); (F) collection cup;
(G) compressed air CO
2
cylinder.
Vet Lab.indb 461 26/03/2019 10:26