Page 53 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 53
The cell (cellula) 35
VetBooks.ir
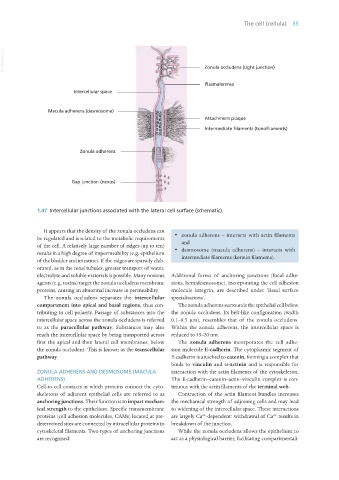
1.47 Intercellular junctions associated with the lateral cell surface (schematic).
It appears that the density of the zonula occludens can
be regulated and is related to the metabolic requirements · zonula adherens – interacts with actin filaments
of the cell. A relatively large number of ridges (up to ten) and
results in a high degree of impermeability (e.g. epithelium · desmosome (macula adherens) – interacts with
of the bladder and intestine). If the ridges are sparsely elab- intermediate filaments (keratin filaments).
orated, as in the renal tubules, greater transport of water,
electrolyte and soluble materials is possible. Many noxious Additional forms of anchoring junctions (focal adhe-
agents (e.g. toxins) target the zonula occludens membrane sions, hemidesmosome), incorporating the cell adhesion
proteins, causing an abnormal increase in permeability. molecule integrin, are described under ‘Basal surface
The zonula occludens separates the intercellular specialisations’.
compartment into apical and basal regions, thus con- The zonula adherens surrounds the epithelial cell below
tributing to cell polarity. Passage of substances into the the zonula occludens. Its belt-like configuration (width
intercellular space across the zonula occludens is referred 0.1–0.5 μm), resembles that of the zonula occludens.
to as the paracellular pathway. Substances may also Within the zonula adherens, the intercellular space is
reach the intercellular space by being transported across reduced to 15–20 nm.
first the apical and then lateral cell membranes, below The zonula adherens incorporates the cell adhe-
the zonula occludens. This is known as the transcellular sion molecule E-cadherin. The cytoplasmic segment of
pathway. E-cadherin is attached to catenin, forming a complex that
binds to vinculin and α-actinin and is responsible for
ZONULA ADHERENS AND DESMOSOME (MACULA interaction with the actin filaments of the cytoskeleton.
ADHERENS) The E-cadherin–catenin–actin–vinculin complex is con-
Cell-to-cell contacts in which proteins connect the cyto- tinuous with the actin filaments of the terminal web.
skeletons of adjacent epithelial cells are referred to as Contraction of the actin filament bundles increases
anchoring junctions. Their function is to impart mechan- the mechanical strength of adjoining cells and may lead
ical strength to the epithelium. Specific transmembrane to widening of the intercellular space. These interactions
proteins (cell adhesion molecules, CAMs) located at pre- are largely Ca -dependent: withdrawal of Ca results in
2+
2+
determined sites are connected by intracellular proteins to breakdown of the junction.
cytoskeletal filaments. Two types of anchoring junctions While the zonula occludens allows the epithelium to
are recognised: act as a physiological barrier, facilitating compartmentali-
Vet Histology.indb 35 16/07/2019 14:54