Page 203 - Manual of Equine Field Surgery
P. 203
Cryptorchid Castration 199
The testicle is removed by emasculation or lig-
ation and transection. Some testicles will not be
able to be exteriorized sufficiently to effectively
· Inguinal extension apply emasculators and will require ligation. If the
of the gubernaculum
vaginal ring has been opened or is wider than one
Vaginal process finger width, the superficial inguinal ring should
be closed with No. 2 or 3 synthetic absorbable
suture material in an interrupted pattern. Further
closure of the subcutaneous tissues and skin is
optional.
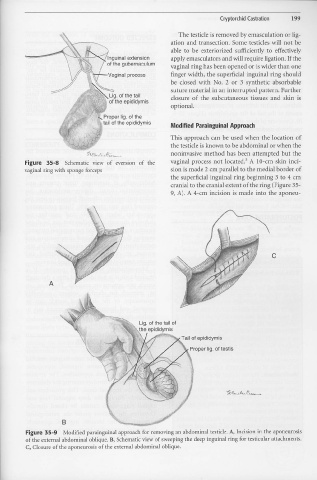
Modified Parainguinal Approach
This approach can be used when the location of
the testicle is known to be abdominal or when the
noninvasive method has been attempted but the
1t.t,:;;,,..,,t;,~J; <.Vlo--
5
Figure 35-8 Schematic view of eversion of the vaginal process not located. A 10-cm skin inci-
vaginal ring with sponge forceps sion is made 2 cm parallel to the medial border of
the superficial inguinal ring beginning 3 to 4 cm
cranial to the cranial extent of the ring (Figure 35-
9, A). A 4-cm incision is made into the aponeu-
c
A
Tail of epididymis
Proper lig. of testis
B
Figure 35-9 Modified parainguinal approach for removing an abdominal testicle. A, Incision in the aponeurosis
of the external abdominal oblique. B, Schematic view of sweeping the deep inguinal ring for testicular attachments.
C, Closure of the aponeurosis of the external abdominal oblique.