Page 188 - Basic Monitoring in Canine and Feline Emergency Patients
P. 188
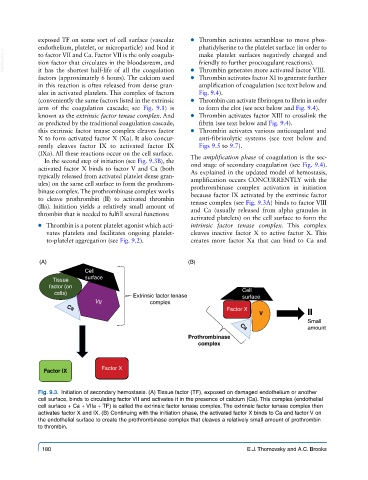
exposed TF on some sort of cell surface (vascular ● ● Thrombin activates scramblase to move phos-
endothelium, platelet, or microparticle) and bind it phatidylserine to the platelet surface (in order to
VetBooks.ir to factor VII and Ca. Factor VII is the only coagula- make platelet surfaces negatively charged and
friendly to further procoagulant reactions).
tion factor that circulates in the bloodstream, and
it has the shortest half-life of all the coagulation
● ● Thrombin activates factor XI to generate further
factors (approximately 6 hours). The calcium used ● ● Thrombin generates more activated factor VIII.
in this reaction is often released from dense gran- amplification of coagulation (see text below and
ules in activated platelets. This complex of factors Fig. 9.4).
(conveniently the same factors listed in the extrinsic ● ● Thrombin can activate fibrinogen to fibrin in order
arm of the coagulation cascade; see Fig. 9.1) is to form the clot (see text below and Fig. 9.4).
known as the extrinsic factor tenase complex. And ● ● Thrombin activates factor XIII to crosslink the
as predicted by the traditional coagulation cascade, fibrin (see text below and Fig. 9.4).
this extrinsic factor tenase complex cleaves factor ● ● Thrombin activates various anticoagulant and
X to form activated factor X (Xa). It also concur- anti-fibrinolytic systems (see text below and
rently cleaves factor IX to activated factor IX Figs 9.5 to 9.7).
(IXa). All these reactions occur on the cell surface.
In the second step of initiation (see Fig. 9.3B), the The amplification phase of coagulation is the sec-
activated factor X binds to factor V and Ca (both ond stage of secondary coagulation (see Fig. 9.4).
typically released from activated platelet dense gran- As explained in the updated model of hemostasis,
ules) on the same cell surface to form the prothrom- amplification occurs CONCURRENTLY with the
binase complex. The prothrombinase complex works prothrombinase complex activation in initiation
to cleave prothrombin (II) to activated thrombin because factor IX activated by the extrinsic factor
(IIa). Initiation yields a relatively small amount of tenase complex (see Fig. 9.3A) binds to factor VIII
thrombin that is needed to fulfill several functions: and Ca (usually released from alpha granules in
activated platelets) on the cell surface to form the
● ● Thrombin is a potent platelet agonist which acti- intrinsic factor tenase complex. This complex
vates platelets and facilitates ongoing platelet- cleaves inactive factor X to active factor X. This
to-platelet aggregation (see Fig. 9.2). creates more factor Xa that can bind to Ca and
(A) (B)
Cell
Tissue surface
factor (on
cells) Cell
Extrinsic factor tenase surface
VII complex
Ca Factor X
V II
Small
amount
Ca
Prothrombinase
complex
Factor X
Factor IX
Fig. 9.3. Initiation of secondary hemostasis. (A) Tissue factor (TF), exposed on damaged endothelium or another
cell surface, binds to circulating factor VII and activates it in the presence of calcium (Ca). This complex (endothelial
cell surface + Ca + VIIa + TF) is called the extrinsic factor tenase complex. The extrinsic factor tenase complex then
activates factor X and IX. (B) Continuing with the initiation phase, the activated factor X binds to Ca and factor V on
the endothelial surface to create the prothrombinase complex that cleaves a relatively small amount of prothrombin
to thrombin.
180 E.J. Thomovsky and A.C. Brooks