Page 210 - Basic Monitoring in Canine and Feline Emergency Patients
P. 210
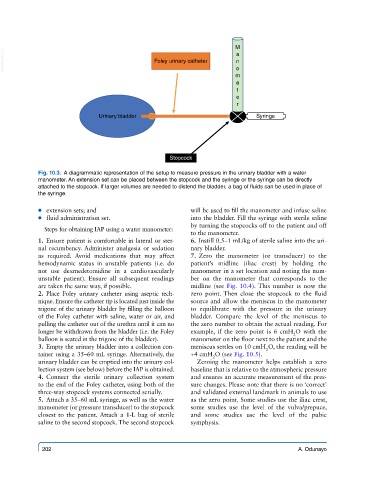
M
VetBooks.ir Foley urinary catheter a
n
o
m
e
t
e
r
Urinary bladder Syringe
Stopcock
Fig. 10.3. A diagrammatic representation of the setup to measure pressure in the urinary bladder with a water
manometer. An extension set can be placed between the stopcock and the syringe or the syringe can be directly
attached to the stopcock. If larger volumes are needed to distend the bladder, a bag of fluids can be used in place of
the syringe.
● ● extension sets; and will be used to fill the manometer and infuse saline
● ● fluid administration set. into the bladder. Fill the syringe with sterile saline
by turning the stopcocks off to the patient and off
Steps for obtaining IAP using a water manometer:
to the manometer.
1. Ensure patient is comfortable in lateral or ster- 6. Instill 0.5–1 mL/kg of sterile saline into the uri-
nal recumbency. Administer analgesia or sedation nary bladder.
as required. Avoid medications that may affect 7. Zero the manometer (or transducer) to the
hemodynamic status in unstable patients (i.e. do patient’s midline (iliac crest) by holding the
not use dexmedetomidine in a cardiovascularly manometer in a set location and noting the num-
unstable patient). Ensure all subsequent readings ber on the manometer that corresponds to the
are taken the same way, if possible. midline (see Fig. 10.4). This number is now the
2. Place Foley urinary catheter using aseptic tech- zero point. Then close the stopcock to the fluid
nique. Ensure the catheter tip is located just inside the source and allow the meniscus in the manometer
trigone of the urinary bladder by filling the balloon to equilibrate with the pressure in the urinary
of the Foley catheter with saline, water or air, and bladder. Compare the level of the meniscus to
pulling the catheter out of the urethra until it can no the zero number to obtain the actual reading. For
longer be withdrawn from the bladder (i.e. the Foley example, if the zero point is 6 cmH O with the
2
balloon is seated in the trigone of the bladder). manometer on the floor next to the patient and the
3. Empty the urinary bladder into a collection con- meniscus settles on 10 cmH O, the reading will be
2
tainer using a 35–60 mL syringe. Alternatively, the +4 cmH O (see Fig. 10.5).
2
urinary bladder can be emptied into the urinary col- Zeroing the manometer helps establish a zero
lection system (see below) before the IAP is obtained. baseline that is relative to the atmospheric pressure
4. Connect the sterile urinary collection system and ensures an accurate measurement of the pres-
to the end of the Foley catheter, using both of the sure changes. Please note that there is no ‘correct’
three-way stopcock systems connected serially. and validated external landmark in animals to use
5. Attach a 35–60 mL syringe, as well as the water as the zero point. Some studies use the iliac crest,
manometer (or pressure transducer) to the stopcock some studies use the level of the vulva/prepuce,
closest to the patient. Attach a 1-L bag of sterile and some studies use the level of the pubic
saline to the second stopcock. The second stopcock symphysis.
202 A. Odunayo