Page 1104 - Clinical Small Animal Internal Medicine
P. 1104
1042 Section 9 Infectious Disease
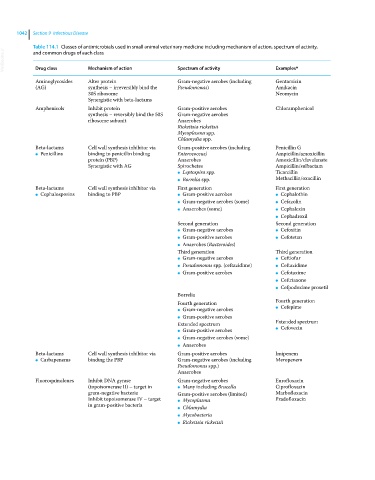
Table 114.1 Classes of antimicrobials used in small animal veterinary medicine including mechanism of action, spectrum of activity,
VetBooks.ir Drug class Mechanism of action Spectrum of activity Examples*
and common drugs of each class
Aminoglycosides Alter protein Gram‐negative aerobes (including Gentamicin
(AG) synthesis – irreversibly bind the Pseudomonas) Amikacin
30S ribosome Neomycin
Synergistic with beta‐lactams
Amphenicols Inhibit protein Gram‐positive aerobes Chloramphenicol
synthesis – reversibly bind the 50S Gram‐negative aerobes
ribosome subunit Anaerobes
Rickettsia rickettsii
Mycoplasma spp.
Chlamydia spp.
Beta‐lactams Cell wall synthesis inhibitor via Gram‐positive aerobes (including Penicillin G
● Penicillins binding to penicillin binding Enterococcus) Ampicillin/amoxicillin
protein (PBP) Anaerobes Amoxicillin/clavulanate
Synergistic with AG Spirochetes Ampicillin/sulbactam
● Leptospira spp. Ticarcillin
● Borrelia spp. Methacillin/oxacillin
Beta‐lactams Cell wall synthesis inhibitor via First generation First generation
● Cephalosporins binding to PBP ● Gram‐positive aerobes ● Cephalothin
● Gram‐negative aerobes (some) ● Cefazolin
● Anaerobes (some) ● Cephalexin
● Cephadroxil
Second generation Second generation
● Gram‐negative aerobes ● Cefoxitin
● Gram‐positive aerobes ● Cefotetan
● Anaerobes (Bacteroides)
Third generation Third generation
● Gram‐negative aerobes ● Ceftiofur
● Pseudomonas spp. (ceftazidime) ● Ceftazidime
● Gram‐positive aerobes ● Cefotaxime
● Ceftriaxone
● Cefpodoxime proxetil
Borrelia
Fourth generation Fourth generation
Cefepime
● Gram‐negative aerobes ●
● Gram‐positive aerobes
Extended spectrum Extended spectrum
Cefovecin
● Gram‐positive aerobes ●
● Gram‐negative aerobes (some)
● Anaerobes
Beta‐lactams Cell wall synthesis inhibitor via Gram‐positive aerobes Imipenem
● Carbapenems binding the PBP Gram‐negative aerobes (including Meropenem
Pseudomonas spp.)
Anaerobes
Fluoroquinolones Inhibit DNA gyrase Gram‐negative aerobes Enrofloxacin
(topoisomerase II) – target in ● Many including Brucella Ciprofloxacin
gram‐negative bacteria Gram‐positive aerobes (limited) Marbofloxacin
Inhibit topoisomerase IV – target ● Mycoplasma Pradofloxacin
in gram‐positive bacteria
● Chlamydia
● Mycobacteria
● Rickettsia rickettsii