Page 1635 - Clinical Small Animal Internal Medicine
P. 1635
177 Behavior Triage for Internists and the General Practitioner 1573
VetBooks.ir Behavior Problem
Aberrant/Abnormal
Normal
- Typical for species, breed, age, etc - Atypical or unexpected for species, breed, age, etc
- “Nuisance”; “unruly” behavior - Includes anxiety and aggression
- Due to lack of training or
appropriate behavioral outlet
- Anxiety and aggression not present
- No physical cause
Examples
Dog: Physical Physical and
- Pulling on leash -Physical illness causing behavioral
- Jumping on people signs Psychological/Behavioral
- Submissive urination - Both physical and psychological/behavioral
Cat: causes are present
- Scratching furniture Examples Examples
- Jumping on counters Dog: Dog:
- Periuria secondary to inadequate -Polyphagia causing pica or
litterbox cleaning stealing food from the trash - Growling at client when lifted into the car
Cat: due to osteoarthritis (physical) and fear of
Client handouts -Housesoiling secondary to a car rides (psychological)
Cat:
urinary tract infection
Training aids - Excessive vocalization caused by
Positive reinforcement-based hyperthyroidism (physical) and reinforced by
training Diagnose and treat physical client offering food (normal behavior)
cause
Trainer Diagnose and treat physical cause
If behavior problem Determine if behavioral component
is normal vs. psychological
persists:
- Reassess original diagnosis and
treatment plan
- Consider combination of physical Psychological
and psychological causes or
development of a secondary - Emotional or neurochemical pathology
behavior problem - Not resolved by training alone
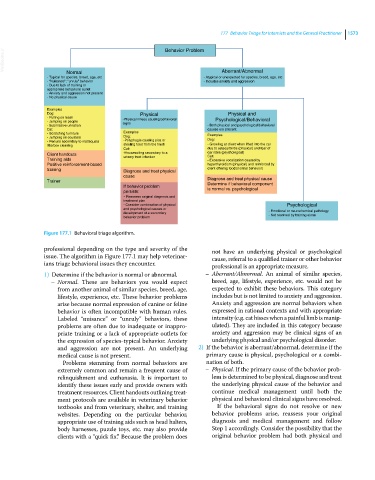
Figure 177.1 Behavioral triage algorithm.
professional depending on the type and severity of the not have an underlying physical or psychological
issue. The algorithm in Figure 177.1 may help veterinar- cause, referral to a qualified trainer or other behavior
ians triage behavioral issues they encounter. professional is an appropriate measure.
1) Determine if the behavior is normal or abnormal. – Aberrant/Abnormal. An animal of similar species,
– Normal. These are behaviors you would expect breed, age, lifestyle, experience, etc. would not be
from another animal of similar species, breed, age, expected to exhibit these behaviors. This category
lifestyle, experience, etc. These behavior problems includes but is not limited to anxiety and aggression.
arise because normal expression of canine or feline Anxiety and aggression are normal behaviors when
behavior is often incompatible with human rules. expressed in rational contexts and with appropriate
Labeled “nuisance” or “unruly” behaviors, these intensity (e.g. cat hisses when a painful limb is manip-
problems are often due to inadequate or inappro- ulated). They are included in this category because
priate training or a lack of appropriate outlets for anxiety and aggression may be clinical signs of an
the expression of species‐typical behavior. Anxiety underlying physical and/or psychological disorder.
and aggression are not present. An underlying 2) If the behavior is aberrant/abnormal, determine if the
medical cause is not present. primary cause is physical, psychological or a combi-
Problems stemming from normal behaviors are nation of both.
extremely common and remain a frequent cause of – Physical. If the primary cause of the behavior prob-
relinquishment and euthanasia. It is important to lem is determined to be physical, diagnose and treat
identify these issues early and provide owners with the underlying physical cause of the behavior and
treatment resources. Client handouts outlining treat- continue medical management until both the
ment protocols are available in veterinary behavior physical and behavioral clinical signs have resolved.
textbooks and from veterinary, shelter, and training If the behavioral signs do not resolve or new
websites. Depending on the particular behavior, behavior problems arise, reassess your original
appropriate use of training aids such as head halters, diagnosis and medical management and follow
body harnesses, puzzle toys, etc. may also provide Step 1 accordingly. Consider the possibility that the
clients with a “quick fix.” Because the problem does original behavior problem had both physical and