Page 724 - Clinical Small Animal Internal Medicine
P. 724
692 Section 7 Diseases of the Liver, Gallbladder, and Bile Ducts
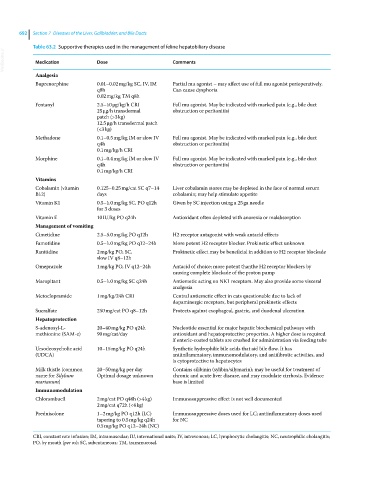
Table 63.2 Supportive therapies used in the management of feline hepatobiliary disease
VetBooks.ir Medication Dose Comments
Analgesia
Buprenorphine 0.01–0.02 mg/kg SC, IV, IM Partial mu agonist – may affect use of full mu agonist perioperatively.
q8h Can cause dysphoria
0.02 mg/kg TM q8h
Fentanyl 2.5–10 μg/kg/h CRI Full mu agonist. May be indicated with marked pain (e.g., bile duct
25 μg/h transdermal obstruction or peritonitis)
patch (>3 kg)
12.5 μg/h transdermal patch
(<3 kg)
Methadone 0.1–0.5 mg/kg IM or slow IV Full mu agonist. May be indicated with marked pain (e.g., bile duct
q4h obstruction or peritonitis)
0.1 mg/kg/h CRI
Morphine 0.1–0.4 mg/kg IM or slow IV Full mu agonist. May be indicated with marked pain (e.g., bile duct
q4h obstruction or peritonitis)
0.1 mg/kg/h CRI
Vitamins
Cobalamin (vitamin 0.125–0.25 mg/cat SC q7–14 Liver cobalamin stores may be depleted in the face of normal serum
B12) days cobalamin; may help stimulate appetite
Vitamin K1 0.5–1.0 mg/kg SC, PO q12h Given by SC injection using a 25 ga needle
for 3 doses
Vitamin E 10 IU/kg PO q24h Antioxidant often depleted with anorexia or malabsorption
Management of vomiting
Cimetidine 2.5–5.0 mg/kg PO q12h H2 receptor antagonist with weak antacid effects
Famotidine 0.5–1.0 mg/kg PO q12–24h More potent H2 receptor blocker. Prokinetic effect unknown
Ranitidine 2 mg/kg PO, SC, Prokinetic effect may be beneficial in addition to H2 receptor blockade
slow IV q8–12h
Omeprazole 1 mg/kg PO, IV q12–24h Antacid of choice; more potent thanthe H2 receptor blockers by
causing complete blockade of the proton pump
Maropitant 0.5–1.0 mg/kg SC q24h Antiemetic acting on NK1 receptors. May also provide some visceral
analgesia
Metoclopramide 1 mg/kg/24h CRI Central antiemetic effect in cats questionable due to lack of
dopaminergic receptors, but peripheral prokinetic effects
Sucralfate 250 mg/cat PO q8–12h Protects against esophageal, gastric, and duodenal ulceration
Hepatoprotection
S‐adenosyl-L- 20–40 mg/kg PO q24h Nucleotide essential for major hepatic biochemical pathways with
methionine (SAM‐e) 90 mg/cat/day antioxidant and hepatoprotective properties. A higher dose is required
if enteric‐coated tablets are crushed for administration via feeding tube
Ursodeoxycholic acid 10–15 mg/kg PO q24h Synthetic hydrophilic bile acids that aid bile flow. It has
(UDCA) antiinflammatory, immunomodulatory, and antifibrotic activities, and
is cytoprotective to hepatocytes
Milk thistle (common 20–50 mg/kg per day Contains silibinin (sylibin/silymarin); may be useful for treatment of
name for Silybum Optimal dosage unknown chronic and acute liver disease, and may modulate cirrhosis. Evidence
marianum) base is limited
Immunomodulation
Chlorambucil 2 mg/cat PO q48h (>4 kg) Immunosuppressive effect is not well documented
2 mg/cat q72h (<4 kg)
Prednisolone 1–2 mg/kg PO q12h (LC) Immunosuppressive doses used for LC; antiinflammatory doses used
tapering to 0.5 mg/kg q24h for NC
0.5 mg/kg PO q12–24h (NC)
CRI, constant rate infusion; IM, intramuscular; IU, international units; IV, intravenous; LC, lymphocytic cholangitis; NC, neutrophilic cholangitis;
PO, by mouth (per os); SC, subcutaneous; TM, transmucosal.