Page 1176 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 1176
VetBooks.ir
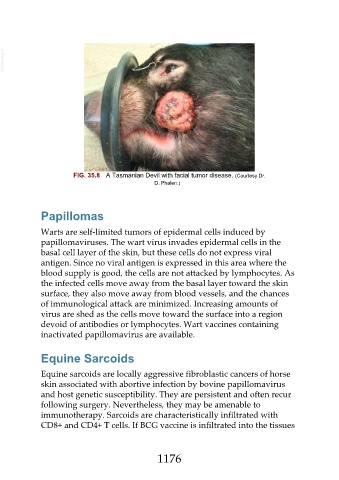
FIG. 35.8 A Tasmanian Devil with facial tumor disease. (Courtesy Dr.
D. Phalen.)
Papillomas
Warts are self-limited tumors of epidermal cells induced by
papillomaviruses. The wart virus invades epidermal cells in the
basal cell layer of the skin, but these cells do not express viral
antigen. Since no viral antigen is expressed in this area where the
blood supply is good, the cells are not attacked by lymphocytes. As
the infected cells move away from the basal layer toward the skin
surface, they also move away from blood vessels, and the chances
of immunological attack are minimized. Increasing amounts of
virus are shed as the cells move toward the surface into a region
devoid of antibodies or lymphocytes. Wart vaccines containing
inactivated papillomavirus are available.
Equine Sarcoids
Equine sarcoids are locally aggressive fibroblastic cancers of horse
skin associated with abortive infection by bovine papillomavirus
and host genetic susceptibility. They are persistent and often recur
following surgery. Nevertheless, they may be amenable to
immunotherapy. Sarcoids are characteristically infiltrated with
CD8+ and CD4+ T cells. If BCG vaccine is infiltrated into the tissues
1176