Page 163 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 163
VetBooks.ir Functions
Sentinel Cells
As described in Chapter 2, macrophages act as sentinel cells. They
are widely distributed through the body and express many
different pattern-recognition receptors (PRRs). They detect and
respond to invading bacteria and viruses as well as tissue damage.
In addition to triggering effective phagocytosis, macrophages
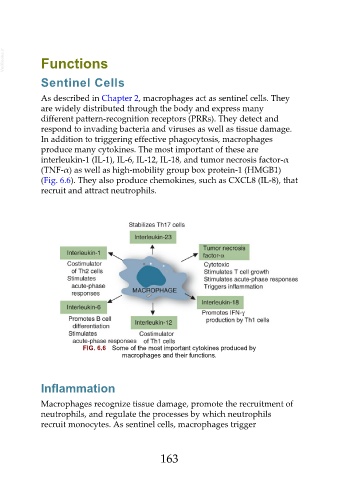
produce many cytokines. The most important of these are
interleukin-1 (IL-1), IL-6, IL-12, IL-18, and tumor necrosis factor-α
(TNF-α) as well as high-mobility group box protein-1 (HMGB1)
(Fig. 6.6). They also produce chemokines, such as CXCL8 (IL-8), that
recruit and attract neutrophils.
FIG. 6.6 Some of the most important cytokines produced by
macrophages and their functions.
Inflammation
Macrophages recognize tissue damage, promote the recruitment of
neutrophils, and regulate the processes by which neutrophils
recruit monocytes. As sentinel cells, macrophages trigger
163