Page 378 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 378
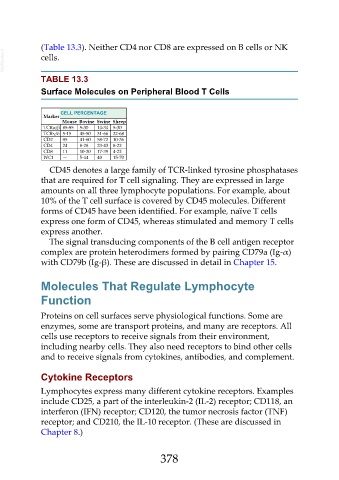
(Table 13.3). Neither CD4 nor CD8 are expressed on B cells or NK
VetBooks.ir cells.
TABLE 13.3
Surface Molecules on Peripheral Blood T Cells
CELL PERCENTAGE
Marker
Mouse Bovine Swine Sheep
TCRα/β 85-95 5-30 14-34 5-30
TCRγ/δ 5-15 45-50 31-66 22-68
CD2 95 41-60 58-72 10-36
CD4 24 8-28 23-43 8-22
CD8 11 10-30 17-39 4-22
WC1 — 5-44 40 15-70
CD45 denotes a large family of TCR-linked tyrosine phosphatases
that are required for T cell signaling. They are expressed in large
amounts on all three lymphocyte populations. For example, about
10% of the T cell surface is covered by CD45 molecules. Different
forms of CD45 have been identified. For example, naïve T cells
express one form of CD45, whereas stimulated and memory T cells
express another.
The signal transducing components of the B cell antigen receptor
complex are protein heterodimers formed by pairing CD79a (Ig-α)
with CD79b (Ig-β). These are discussed in detail in Chapter 15.
Molecules That Regulate Lymphocyte
Function
Proteins on cell surfaces serve physiological functions. Some are
enzymes, some are transport proteins, and many are receptors. All
cells use receptors to receive signals from their environment,
including nearby cells. They also need receptors to bind other cells
and to receive signals from cytokines, antibodies, and complement.
Cytokine Receptors
Lymphocytes express many different cytokine receptors. Examples
include CD25, a part of the interleukin-2 (IL-2) receptor; CD118, an
interferon (IFN) receptor; CD120, the tumor necrosis factor (TNF)
receptor; and CD210, the IL-10 receptor. (These are discussed in
Chapter 8.)
378