Page 18 - AERIAL ACROBATICS & CALISTHENICS VOL. 1 (ENG).pdf
P. 18
1.2 → MUSCULAR CONTRACTION
Understanding the different types of muscle contractions will also help us better plan our training program, since each type of contraction has different advantages and disadvantages with respect to our goals.
A muscular contraction is the process in which tension is generated within muscle tissue in re- sponse to force or load. A muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening, it can be produced without changes in muscle length, or even when the muscle lengthens.
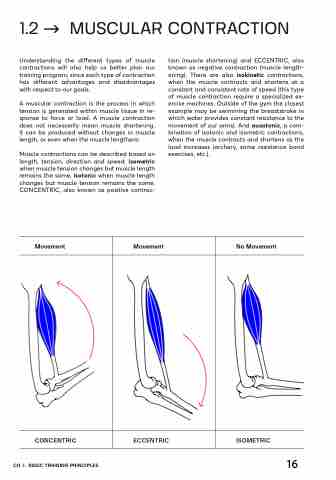
Muscle contractions can be described based on length, tension, direction and speed; isometric when muscle tension changes but muscle length remains the same, isotonic when muscle length changes but muscle tension remains the same, CONCENTRIC, also known as positive contrac-
Movement
tion (muscle shortening) and ECCENTRIC, also known as negative contraction (muscle length- ening). There are also isokinetic contractions, when the muscle contracts and shortens at a constant and consistent rate of speed (this type of muscle contraction require a specialized ex- ercise machines. Outside of the gym the closest example may be swimming the breaststroke in which water provides constant resistance to the movement of our arms). And auxotonic, a com- bination of isotonic and isometric contractions, when the muscle contracts and shortens as the load increases (archery, some resistance band exercises, etc.).
Movement
ECCENTRIC
No Movement
CONCENTRIC
ISOMETRIC
CH. 1. BASIC TRAINING PRINCIPLES
16