Page 19 - GP Spring 2022
P. 19
● Completely repaired congenital heart Although antibiotics are not recommended any dental procedure that can cause bleed-
defect with prosthetic material or de- preoperatively, there may be certain circum- ing and transient bacteremia is expected an-
vice during the first 6 months after the stances in which antibiotics are indicated, tibiotic prophylaxis is recommended.
procedure such as a history of having complications
● Repaired CHD with residual defects at related to joint replacement surgery or the Antibiotic prophylaxis is not suggested for
the site of, or adjacent to, the site of a presence of comorbidities associated with anesthetic injections through noninfected
prosthetic patch or device immunosuppression, such as poorly con- tissue, taking dental radiographs, placement
of removable prosthodontic or orthodontic
trolled diabetes, diseases affecting the im-
● Cardiac transplant recipients with val- mune system, or taking medications that can appliances, adjustment of orthodontic appli-
vulopathy alter the patient’s immunological response. ances, placement of orthodontic brackets,
● Left ventricular assist devices (LAVDs) shedding of primary teeth, and bleeding
or implantable heart devices The reason for the changes is that the chance from trauma to the lips or oral mucosa.
of oral bacteremia being related to joint in-
Antibiotic prophylaxis is not currently fections is extremely low, with no evidence Antibiotic Regimen
recommended for: for an association. In previous guidelines, clindamycin was
recommended as the antibiotic of choice for
● Implantable electronic devices such as What is known is that oral bacteremia fre- patients who were allergic to penicillin, and
pacemakers or similar devices quently occurs secondary to activities of other cephalosporins, and could take oral
● Septal defect closure devices with suc- daily living such as tooth brushing and medications. This recommendation has
eating, and virtually all dental office proce-
changed, given the risks associated with its
cessful repairs dures have the potential to create bactere- use (such as severe diarrhea and Clostridium
● Peripheral vascular grafts and patches mia. difficile colitis). According to the AHA,
16
( including those used in hemodialysis) cephalexin (or other first- or second-gener-
● Coronary artery stents or other vascular One can check the AAOS website and re- ation cephalosporins), azithromycin, clar-
view the Appropriate Use Criteria: Manage-
ithromycin, or doxycycline should be cho-
stents ment of Patients with Orthopedic Implants sen instead. However, the recommendations
● Central Nervous System (CNS) ven- Undergoing Dental Procedures Tool (2016) indicate that cephalosporins should not be
triculoatrial shunts to support the decision-making. used if the cross-reactivity is not confirmed.
● Vena cava filters (https://aaos.webauthor.com/go/auc/terms. Patients who are allergic to penicillin and
● Pledgets cfm?actionxm=Terms&auc_id=224995. cannot tolerate an oral antibiotic should use
cefazolin or ceftriaxone intramuscular (IM)
Patients with Prosthetic Joint/ Implants If the nature of surgical complications is un- or intravascular (IV) injection. In addition,
According to the most recent guidelines, known, it is reasonable to consult with the patients who report a history of hypersen-
patients with prosthetic joint implants do orthopedic surgeon. The recommendations sitivity reactions to penicillin or ampicillin
not require antibiotic prophylaxis before for prophylaxis are indicated for invasive should avoid using cephalosporins altogeth-
undergoing invasive dental treatments. The dental procedures similar to those proposed er and the use of another class of IV antibi-
evidence for the decision is provided by the by the AHA. otic should be discussed with the physician
ADA (American Dental Association) clini- (IV Azithromycin) (See Table 1 for current
cal practice guideline published in 2015 and Antibiotic prophylaxis is suggested for all regimen).
was based on a systematic review the year dental procedures that involve manipulation
14
before in conjunction with the American of gingival tissue or the periapical region of There are certain instances in which a
15
Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons (AAOS). teeth or perforation of the oral mucosa. For patient may have forgotten to take the
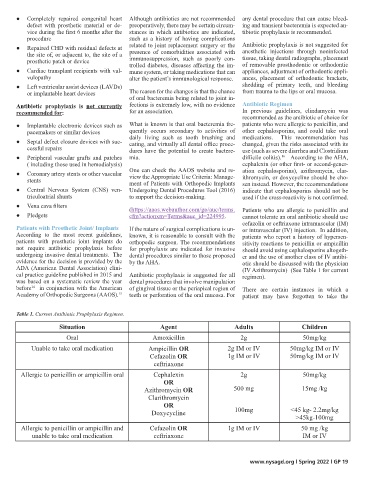
Table 1. Current Antibiotic Prophylaxis Regimen.
Situation Agent Adults Children
Oral Amoxicillin 2g 50mg/kg
Unable to take oral medication Ampicillin OR 2g IM or IV 50mg/kg IM or IV
Cefazolin OR 1g IM or IV 50mg/kg IM or IV
ceftriaxone
Allergic to penicillin or ampicillin oral Cephalexin 2g 50mg/kg
OR
Azithromycin OR 500 mg 15mg /kg
Clarithromycin
OR
Doxycycline 100mg <45 kg- 2.2mg/kg
>45kg-100mg
Allergic to penicillin or ampicillin and Cefazolin OR 1g IM or IV 50 mg /kg
unable to take oral medication ceftriaxone IM or IV
www.nysagd.org l Spring 2022 l GP 19