Page 5 - UKBM 3.8 NARRATIVE
P. 5
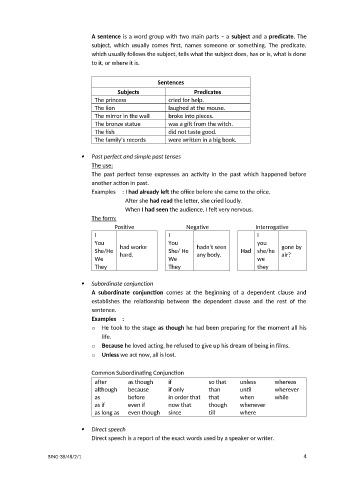
A sentence is a word group with two main parts – a subject and a predicate. The
subject, which usually comes first, names someone or something. The predicate,
which usually follows the subject, tells what the subject does, has or is, what is done
to it, or where it is.
Sentences
Subjects Predicates
The princess cried for help.
The lion laughed at the mouse.
The mirror in the wall broke into pieces.
The bronze statue was a gift from the witch.
The fish did not taste good.
The family’s records were written in a big book.
Past perfect and simple past tenses
The use:
The past perfect tense expresses an activity in the past which happened before
another action in past.
Examples : I had already left the office before she came to the ofice.
After she had read the letter, she cried loudly.
When I had seen the audience, I felt very nervous.
The form:
Positive Negative Interrogative
I I I
You You you
She/He had worke She/ He hadn’t seen Had she/he gone by
any body.
hard.
air?
We We we
They They they
Subordinate conjunction
A subordinate conjunction comes at the beginning of a dependent clause and
establishes the relationship between the dependent clause and the rest of the
sentence.
Examples :
o He took to the stage as though he had been preparing for the moment all his
life.
o Because he loved acting, he refused to give up his dream of being in films.
o Unless we act now, all is lost.
Common Subordinating Conjunction
after as though if so that unless whereas
although because if only than until wherever
as before in order that that when while
as if even if now that though whenever
as long as even though since till where
Direct speech
Direct speech is a report of the exact words used by a speaker or writer.
BING-38/48/2/1 4