Page 182 - Innovative Professional Development Methods and Strategies for STEM Education
P. 182
Identifying the Target Needs of Non-Native Subject Teachers
reading was found to be demanding by these subject teachers as majority of them stated they needed a
lot of or some practice on them (for example, reading books, articles and reading the materials related
to their fields on the websites (n = 31, 86.1%), reading lesson materials and teacher’s book (n = 30,
83.4%). These findings may indicate a lack in terms of vocabulary knowledge related to their own subject
fields. Similarly, these teachers might also be unfamiliar with the genres used in these reading materials.
However, to determine the exact reasons for this perceived lack, more in depth research needs to be done.
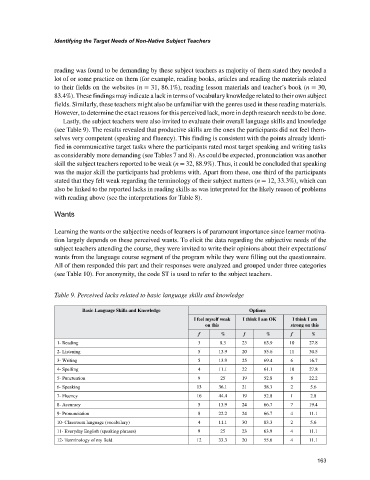
Lastly, the subject teachers were also invited to evaluate their overall language skills and knowledge
(see Table 9). The results revealed that productive skills are the ones the participants did not feel them-
selves very competent (speaking and fluency). This finding is consistent with the points already identi-
fied in communicative target tasks where the participants rated most target speaking and writing tasks
as considerably more demanding (see Tables 7 and 8). As could be expected, pronunciation was another
skill the subject teachers reported to be weak (n = 32, 88.9%). Thus, it could be concluded that speaking
was the major skill the participants had problems with. Apart from these, one third of the participants
stated that they felt weak regarding the terminology of their subject matters (n = 12, 33.3%), which can
also be linked to the reported lacks in reading skills as was interpreted for the likely reason of problems
with reading above (see the interpretations for Table 8).
Wants
Learning the wants or the subjective needs of learners is of paramount importance since learner motiva-
tion largely depends on these perceived wants. To elicit the data regarding the subjective needs of the
subject teachers attending the course, they were invited to write their opinions about their expectations/
wants from the language course segment of the program while they were filling out the questionnaire.
All of them responded this part and their responses were analyzed and grouped under three categories
(see Table 10). For anonymity, the code ST is used to refer to the subject teachers.
Table 9. Perceived lacks related to basic language skills and knowledge
Basic Language Skills and Knowledge Options
I feel myself weak I think I am OK I think I am
on this strong on this
f % f % f %
1- Reading 3 8.3 23 63.9 10 27.8
2- Listening 5 13.9 20 55.6 11 30.5
3- Writing 5 13.9 25 69.4 6 16.7
4- Spelling 4 11.1 22 61.1 10 27.8
5- Punctuation 9 25 19 52.8 8 22.2
6- Speaking 13 36.1 21 58.3 2 5.6
7- Fluency 16 44.4 19 52.8 1 2.8
8- Accuracy 5 13.9 24 66.7 7 19.4
9- Pronunciation 8 22.2 24 66.7 4 11.1
10- Classroom language (vocabulary) 4 11.1 30 83.3 2 5.6
11- Everyday English (speaking phrases) 9 25 23 63.9 4 11.1
12- Terminology of my field 12 33.3 20 55.6 4 11.1
163