Page 210 - IGC BOOK
P. 210
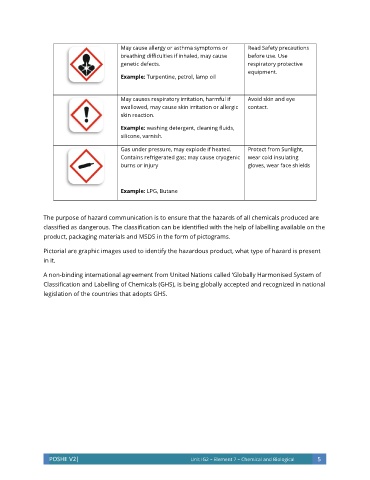
May cause allergy or asthma symptoms or Read Safety precautions
breathing difficulties if inhaled, may cause before use. Use
genetic defects. respiratory protective
equipment.
Example: Turpentine, petrol, lamp oil
May causes respiratory irritation, harmful if Avoid skin and eye
swallowed, may cause skin irritation or allergic contact.
skin reaction.
Example: washing detergent, cleaning fluids,
silicone, varnish.
Gas under pressure, may explode if heated. Protect from Sunlight,
Contains refrigerated gas; may cause cryogenic wear cold insulating
burns or injury gloves, wear face shields
Example: LPG, Butane
The purpose of hazard communication is to ensure that the hazards of all chemicals produced are
classified as dangerous. The classification can be identified with the help of labelling available on the
product, packaging materials and MSDS in the form of pictograms.
Pictorial are graphic images used to identify the hazardous product, what type of hazard is present
in it.
A non-binding international agreement from United Nations called ‘Globally Harmonised System of
Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS), is being globally accepted and recognized in national
legislation of the countries that adopts GHS.
POSHE V2| Unit IG2 – Element 7 – Chemical and Biological 5
Agents