Page 187 - Pharmacognosy 2 PG303 (1)
P. 187
Pharmacognosy-2 (PG303) Level 2 Clinical Pharmacy-Pharm D
diameter, occur in the parenchyma and also a few prisms. The xylem contains
numerous vessels with bordered pits and also thick-walled xylem fibers. The
cells of the cork are thin-walled and usually lignified as well as suberized.
The resin or latex cells occur abundantly in the parenchyma of the phloem
and the resin stains yellow with iodine water.
Constituents
Like jalap, the chief constituent of Orizaba jalap root is the resin it
contains, other constituents of less importance are sugar, β-methyl-aesculetin,
dihydroxycinnamic acid, fatty acids, phytosterol, starch and calcium oxalate. The
amount of crude resin varies from 6-22 %, averaging 12-18 %.
Crude lpomoea resin, often known as Scammony resin, is prepared by
exhaustion coarsely powdered lpomoea by percolation with alcohol, 90 %,
rernoving the alcohol by evaporation, washing the residue with boiling water and
drying it. The resin occurs in commerce as a pale brown powder or in the form of
translucent, brittle brown pieces, having a characteristic odor and an acrid taste.
The crude resin is a very complex mixture. It contains about 6 % of fatty
substances, 64.8 % of resin soluble in ether. The ether-soluble portion is not
identical with the ether-soluble portion of jalap resin. By alkaline hydrolysis it
yields ipuranol, methylbutyric acid, tiglic acid and a product which, by acid
hydrolysis, yields dextrose, a methylpentose, jalapinolic acid and methyl
jalapinolate. The chief constituents, therefore, appear to be the glucoside and
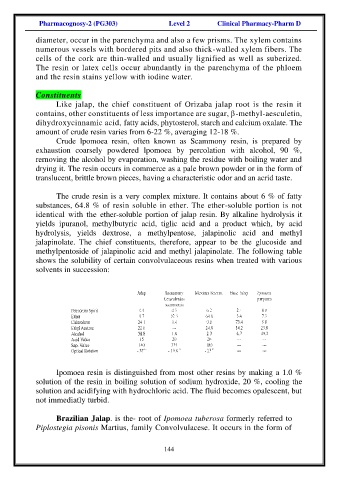
methylpentoside of jalapinolic acid and methyl jalapinolate. The following table
shows the solubility of certain convolvulaceous resins when treated with various
solvents in succession:
Ipomoea resin is distinguished from most other resins by making a 1.0 %
solution of the resin in boiling solution of sodium hydroxide, 20 %, cooling the
solution and acidifying with hydrochloric acid. The fluid becomes opalescent, but
not immediatly turbid.
Brazilian Jalap. is the- root of Ipomoea tuberosa formerly referred to
Piplostegia pisonis Martius, family Convolvulacese. It occurs in the form of
144