Page 318 - Pharmacognosy 2 PG303 (1)
P. 318
Pharmacognosy-2 (PG303) Level 2 Clinical Pharmacy-Pharm D
faintly with HCl and add few drops of FeCl 3 T.S.; a brown red to purplish-red
color is produced. This color is not destroyed by dilute HCl or by HgCl 2 T.S.
(c.f. Thiocyanates).
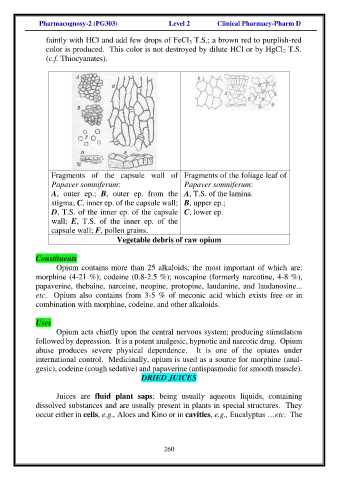
Fragments of the capsule wall of Fragments of the foliage leaf of
Papaver somniferum: Papaver somniferum:
A, outer ep.; B, outer ep. from the A, T.S. of the lamina.
stigma; C, inner ep. of the capsule wall; B, upper ep.;
D, T.S. of the inner ep. of the capsule C, lower ep.
wall; E, T.S. of the inner ep. of the
capsule wall; F, pollen grains.
Vegetable debris of raw opium
Constituents
Opium contains more than 25 alkaloids; the most important of which are:
morphine (4-21 %); codeine (0.8-2.5 %); noscapine (formerly narcotine, 4-8 %),
papaverine, thebaine, narceine, neopine, protopine, laudanine, and laudanosine...
etc. Opium also contains from 3-5 % of meconic acid which exists free or in
combination with morphine, codeine, and other alkaloids.
Uses
Opium acts chiefly upon the central nervous system; producing stimulation
followed by depression. It is a potent analgesic, hypnotic and narcotic drug. Opium
abuse produces severe physical dependence. It is one of the opiates under
international control. Medicinally, opium is used as a source for morphine (anal-
gesic), codeine (cough sedative) and papaverine (antispasmodic for smooth muscle).
DRIED JUICES
Juices are fluid plant saps; being usually aqueous liquids, containing
dissolved substances and are usually present in plants in special structures. They
occur either in cells, e.g., Aloes and Kino or in cavities, e.g., Eucalyptus …etc. The
260