Page 39 - Banking Finance November 2019
P. 39
ARTICLE
B. If the instrument will or may be understanding of financial instrument as per IND AS vis Indian GAAP :-
settled in the issuer's own equity 1. Statutory Liability- Not a financial instrument as per IND AS
instrument it is: 2. Advance for purchase of goods - Not a financial instrument as per IND AS
Y A non- derivative that include
no contractual obligation for 3. Liability for damages under a court case - Not a financial instrument as per
the issuer to deliver a variable IND AS.
number of its own equity 4. USD - INR Option in the books of option buyer - A financial instrument and
instrument an asset in the books of option buyer.
or 5. Trade Receivable - Financial Asset.
Y A Derivative that will be 6. Gold Bullion - Not a financial instrument as per IND AS as no contractual
settled only "by the issuer" obligation.
exchanging a fixed amount of 7. Advance payment of tax - Not a financial instrument as per IND AS as no
cash or another financial asset contractual obligation.
for a fixed number of its own
equity instruments.
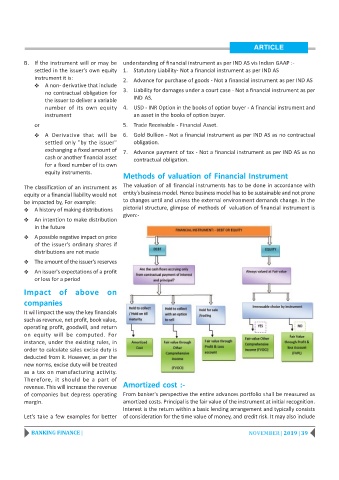
Methods of valuation of Financial Instrument
The classification of an instrument as The valuation of all financial instruments has to be done in accordance with
equity or a financial liability would not entity's business model. Hence business model has to be sustainable and not prone
be impacted by, For example: to changes until and unless the external environment demands change. In the
Y A history of making distributions pictorial structure, glimpse of methods of valuation of financial instrument is
given:-
Y An intention to make distribution
in the future
Y A possible negative impact on price
of the issuer's ordinary shares if
distributions are not made
Y The amount of the issuer's reserves
Y An issuer's expectations of a profit
or loss for a period
Impact of above on
companies
It will impact the way the key financials
such as revenue, net profit, book value,
operating profit, goodwill, and return
on equity will be computed. For
instance, under the existing rules, in
order to calculate sales excise duty is
deducted from it. However, as per the
new norms, excise duty will be treated
as a tax on manufacturing activity.
Therefore, it should be a part of
revenue. This will increase the revenue Amortized cost :-
of companies but depress operating From banker's perspective the entire advances portfolio shall be measured as
margin. amortized costs. Principal is the fair value of the instrument at initial recognition.
Interest is the return within a basic lending arrangement and typically consists
Let's take a few examples for better of consideration for the time value of money, and credit risk. It may also include
BANKING FINANCE | NOVEMBER | 2019 | 39