Page 53 - Banking Finance October 2025
P. 53
ARTICLE
In such an environment, relying on ad-hoc controls is no 2. ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Li-
longer sufficient. A structured and standardized framework brary)
helps banks adopt a proactive, rather than reactive, ap-
proach to risks.
Understanding the Frameworks
1. NIST Cybersecurity Framework
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) is one of the most
widely adopted global standards for managing cybersecurity
risk. It is built around five key functions: Identify, Protect,
Detect, Respond, and Recover.
Identify: Banks can assess critical assets, data flows,
and risk exposures.
Protect: Safeguards such as encryption, access manage-
ment, and security training are implemented.
Detect: Continuous monitoring systems are established
to recognize anomalies.
Respond: Incident response protocols are designed for
quick containment.
Recover: Plans are created for restoring operations and
maintaining business continuity.
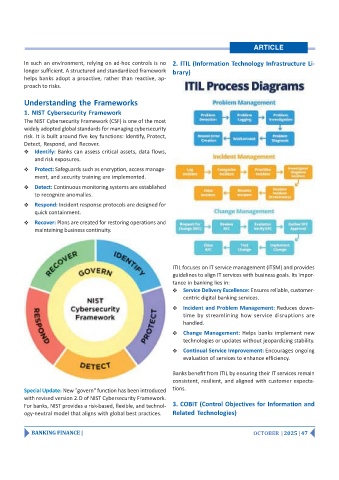
ITIL focuses on IT service management (ITSM) and provides
guidelines to align IT services with business goals. Its impor-
tance in banking lies in:
Service Delivery Excellence: Ensures reliable, customer-
centric digital banking services.
Incident and Problem Management: Reduces down-
time by streamlining how service disruptions are
handled.
Change Management: Helps banks implement new
technologies or updates without jeopardizing stability.
Continual Service Improvement: Encourages ongoing
evaluation of services to enhance efficiency.
Banks benefit from ITIL by ensuring their IT services remain
consistent, resilient, and aligned with customer expecta-
Special Update: New "govern" function has been introduced tions.
with revised version 2.O of NIST Cybersecurity Framework.
For banks, NIST provides a risk-based, flexible, and technol- 3. COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and
ogy-neutral model that aligns with global best practices. Related Technologies)
BANKING FINANCE | OCTOBER | 2025 | 47